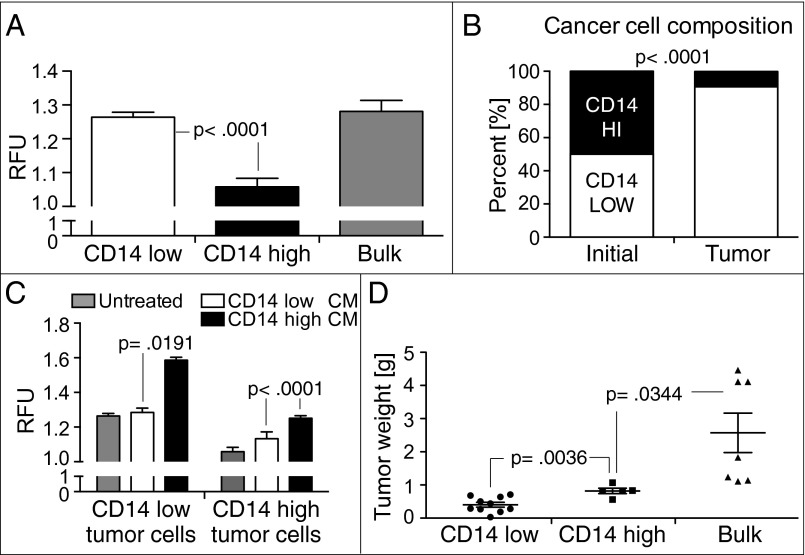
Fig. 4.
Inflammation mediators from CD14-high BC cells promote tumor proliferation. (A) Proliferation rate of BC subpopulations measured by BrdU incorporation (n = 6) (mean and SEM; P < 0.0001). (B) Equal numbers of CD14-high and CD14-low subpopulations were implanted into mice. Relative frequency of each subpopulation in the ectopic tumors after 1 mo is shown (n = 4) (mean; P < 0.0001). (C) Proliferation rate of CD14-high and -low BC subpopulations in exogenously added tumor CMs (n = 6) (mean and SEM; P < 0.0001). (D) Growth of ectopic tumors formed by s.c. injection of CD14-high (n = 5), CD14-low (n = 10), and bulk-unsorted MB49 subpopulations into syngeneic wild-type mice (n = 7) after 4 wk (mean and SEM; P = 0.0344).