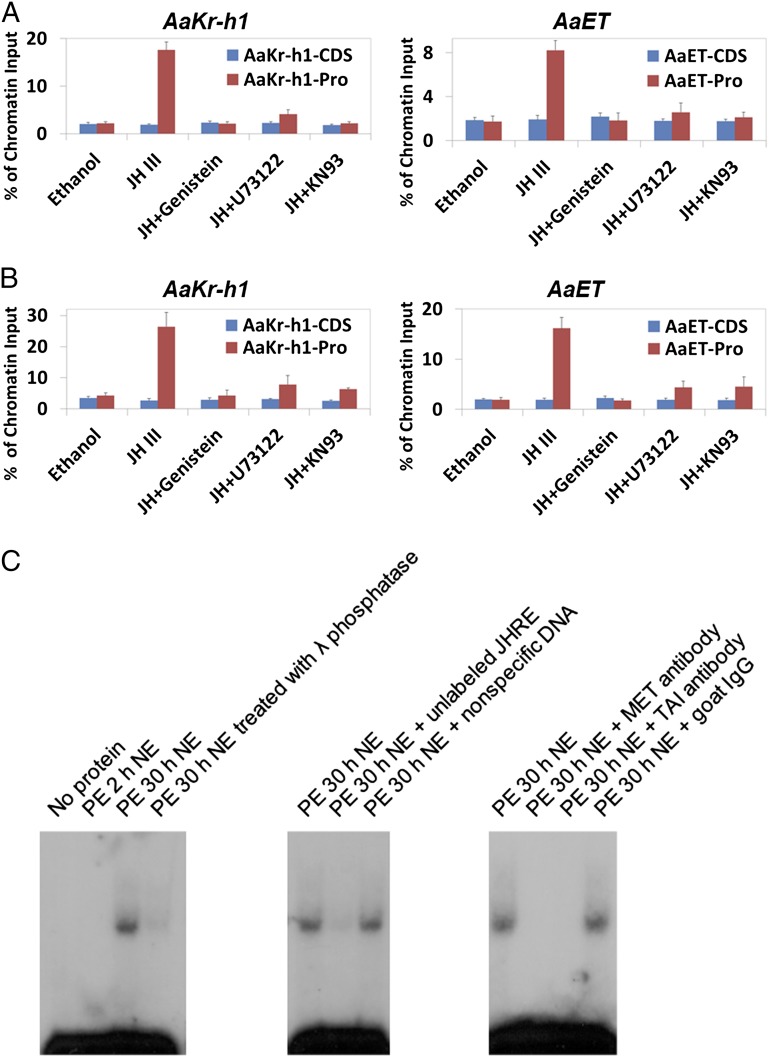
Fig. 7.
The PLC pathway affects binding of the MET/TAI complex to the JH-responsive promoters. Abdomens from newly emerged mosquitoes were cultured in vitro with Genistein, U73122, and KN93 for 1 h. After 1 µM JH-III was added to the medium, culture continued for additional 3 h. (A and B) ChIP assays were performed using antibodies against AaMET (A) and AaTAI (B). Precipitated DNA was examined using real-time PCR. For each JH target gene, two pairs of primers were designed to amplify the proximal promoter (Pro) region and the coding DNA sequence (CDS) region. Results are presented as a percentage of input chromatin and represent mean values ± SDs of two independent experiments. (C) Dephosphorylation inhibited the binding of MET/TAI to JHRE. Nuclear proteins were extracted from the abdomens of adult female mosquitoes at the indicated time points and were incubated in vitro with the [32P]-labeled JHRE from the AaET gene (AaET_JHRE1). For phosphatase treatment, nuclear proteins extracted from mosquitoes at 30 h PE were incubated with 1 U/μL λ phosphatase for 1 h on ice. For competition experiments, nuclear extracts (NE) were incubated with an approximate 100× molar excess of unlabeled probe or a nonspecific double-stranded oligonucleotide for 20 min before incubation with the labeled probe. Binding of AaMET/AaTAI to the probe was verified by adding polyclonal antibodies against AaMET and AaTAI directly to the binding reactions. Nonspecific goat IgG was used as a negative control.