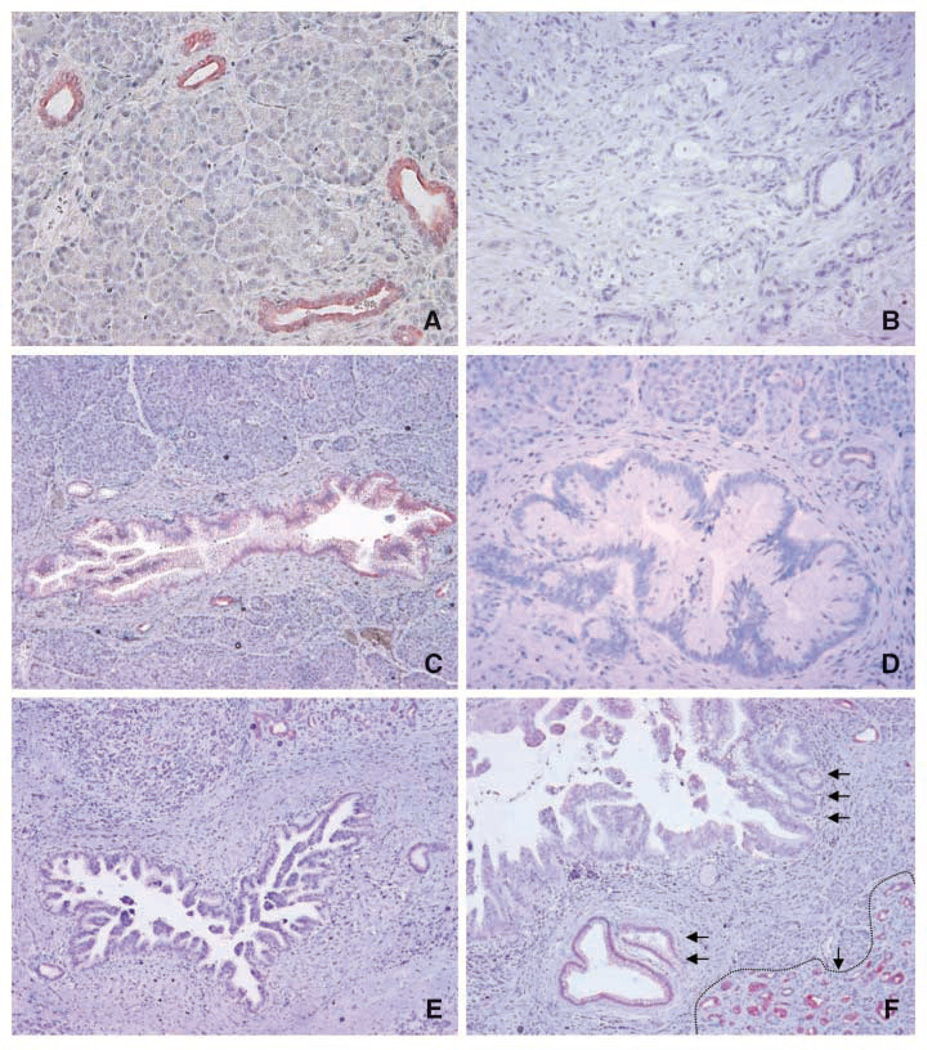
Figure 1.
Representative micrographs showing HPK1 expression in benign pancreatic tissue, invasive PDA, and PanIN lesions of different grades. A, benign pancreatic ducts that were strongly positive for HPK1, but no staining present in pancreatic acinar cells. B, invasive PDA with negative staining for HPK1. C, PanIN1 lesion with weak positive staining for HPK1. D and E, PanIN2 and PanIN3 lesions with negative staining for HPK1, respectively. F, progressive loss of HPK1 with the progression of PanIN lesions: strong positive staining for HPK1 in benign pancreatic ducts (single arrow with dotted line at the right lower corner), weak positive staining for HPK1 in PanIN1 lesions (double arrows), and negative staining in high-grade PanIN3 lesions (triple arrows).The strong positive staining for HPK1 in the adjacent benign pancreatic ducts served as internal positive control in C to E.Original magnification, ×100.