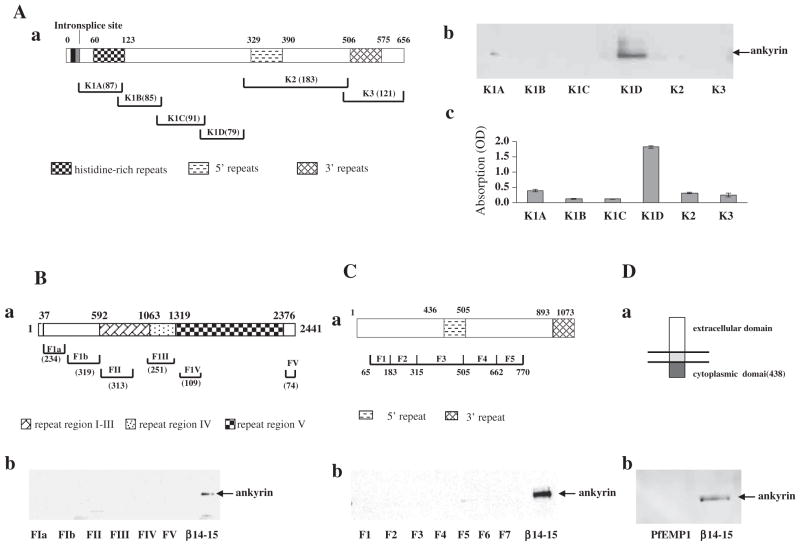
Fig. 1.
Association of malaria proteins with ankyrin R. (A) Binding of ankyrin R to KAHRP fragments. Schematic representation of KAHRP (a). The binding between ankyrin R and KAHRP fragments was assessed by pull-down (b) and ELISA assay (c). Note that ankyrin R bound to only the K1D fragment of the KAHRP. (B) Binding of ankyrin R to PfEMP3 fragments. Schematic representation of PfEMP3 (a). The binding between ankyrin R and PfEMP3 fragments was assessed by pull-down (b). Repeats 14–15 fragment of β-spectrin was used as a positive control for ankyrin R binding. (C) Binding of ankyrin R to RESA fragments. Schematic representation of RESA (a). The binding between ankyrin R and RESA fragments was assessed by pull-down (b). Repeats 14–15 fragment of β-spectrin was used as a positive control for ankyrin R binding. (D) Binding of ankyrin R to the cytoplasmic domain of PfEMP1. Schematic representation of PfEMP1 (a). The binding between ankyrin R and cytoplasmic domain of PfEMP1 was assessed by pull-down (b). Repeats 14–15 fragment of β-spectrin was used as a positive control for ankyrin R binding. Amino acid residue numbers and the lengths of fragments are indicated.