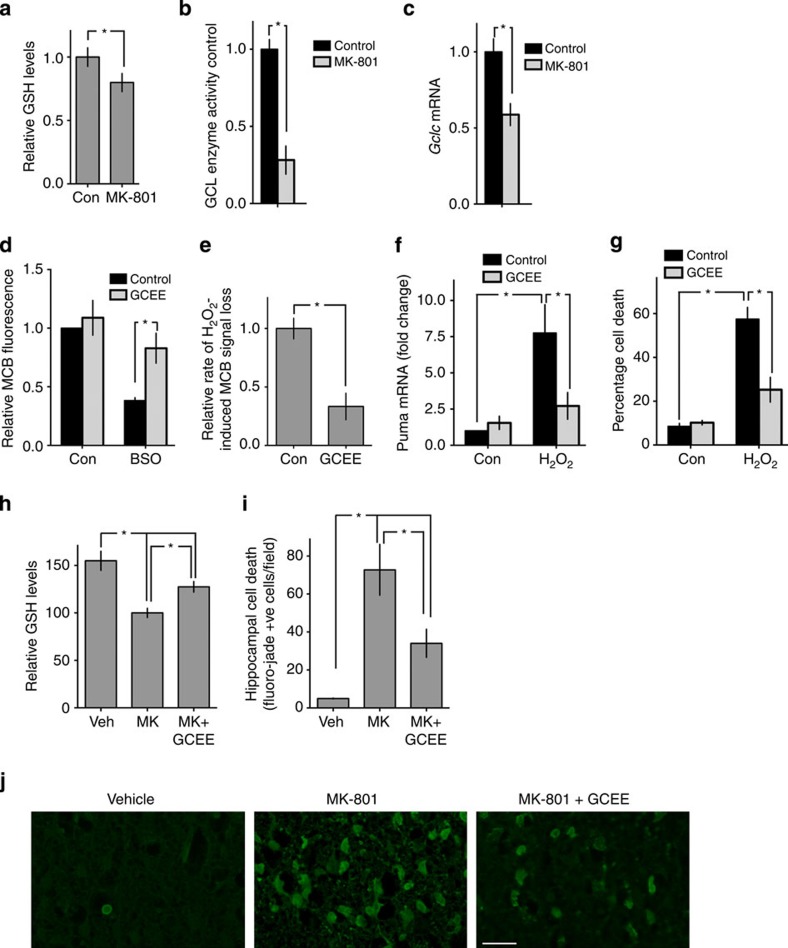
Figure 5. Deleterious effects of NMDAR blockade in vivo are due to Gclc transcriptional repression.
(a) Blockade of NMDARs causes a reduction of cortical GSH content in vivo. Cortical GSH levels measured in P6 rat pups 24 h after the first injection. *P=0.0495, one-tailed t-test (n=4). (b,c) Blockade of NMDARs reduces GCL enzyme activity and Gclc expression in vivo. Rat pups treated as in Fig. 4a and cortical GCL activity (b) and Gclc expression (c) were measured at 12 h and expressed relative to the mean of the control group. P=0.0006 (b), 0.0042 (c) (n=4). (d) GCEE sustains GSH levels in the presence of GCL inhibitor. Neurons were treated with GCEE (1 mM) for 1 h, followed by 200 μM BSO for 24 h, followed by MCB assay. *P=0.0002 (n=9 (con), n=5 (BSO)). (e) GCEE attenuates GSH depletion by oxidative insult. Neurons were treated for 1 h with GCEE then rate of decline in GS-bimane fluorescence induced by 250 μM H2O2 measured. *P=0.0070 (n=4). (f,g) GCEE attenuates oxidative stress-induced Puma mRNA expression and cell death. Neurons were preincubated ±GCEE for 1 h, then treated with 100 μM H2O2 and either Puma levels. *P=0.0086, 0.047 (f) n=9 (con), n=5 (GCEE)) or cell death analysed.*P=0.0110, 0.0217 (n=4 (H2O2, n=3 (Con)). (h) GCEE rescues NMDAR blockade dependent forebrain GSH depletion in vivo. P6 Rat pups were injected twice at 0 and 8 h and cortical GSH levels measured at 24 h, normalized to protein content and expressed relative to MK-801 treated samples. *P=<0.0001, 0.0105, 0.0087, 1WA-Fph (n=8,9,9 for Veh, MK, MK+GCEE respectively). (i,j) GCEE rescues neurons from MK-801 induced cell death in vivo. P6 Rat pups were injected twice at 0 and 8 h and killed 24 h post first injection, followed by Fluoro-Jade staining-based analysis of neurodegeneration within the hippocampus. *P=<0.0001, 0.0105, 0.0087, 1WA-Fph (n=9, 11, 11 for Veh, MK and MK+GCEE, respectively). Scale bar, 30 μm.