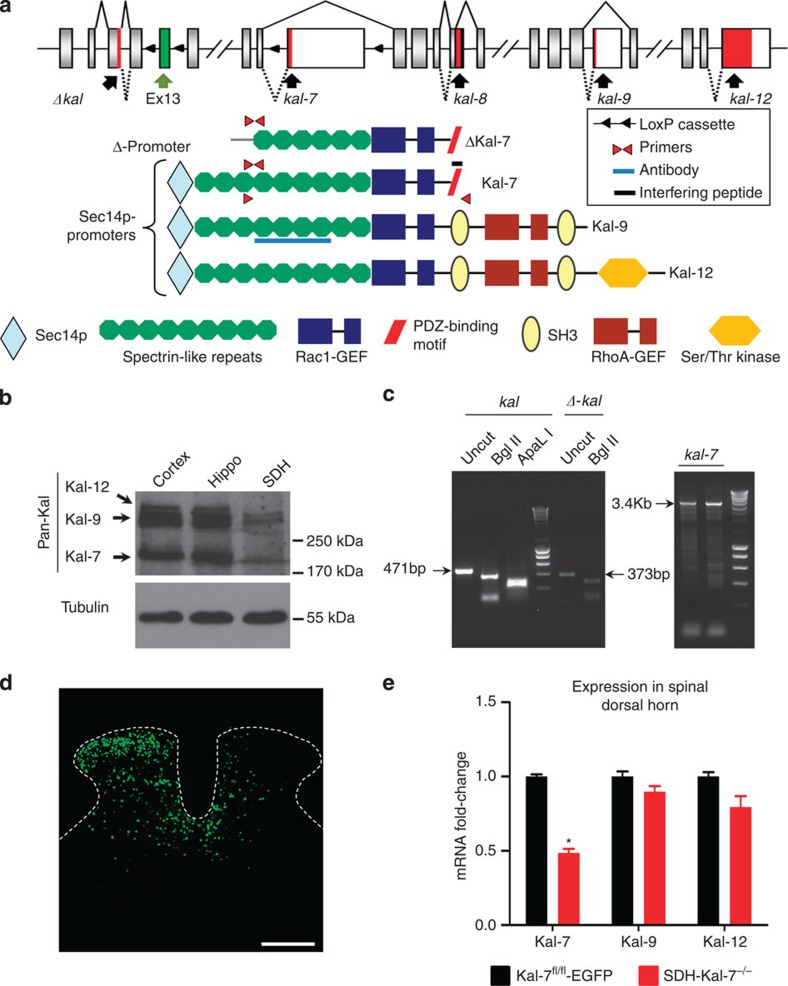
Figure 1. Expression of diverse Kalirins in the spinal dorsal horn and specific knockout of Kal-7 in spinal neurons.
(a) Structure of the mouse Kalrn gene and the major protein products resulting via alternative splicing. Sites targeted by the reagents used in this study are shown. (b) Western blotting with antibody against the spectrin-repeat region detects expression of Kalirin in the spinal dorsal horn (SDH), with lysates from cortex and hippocampus as positive controls. (c) Transcripts for truncated or full-length Kalirins together with full-length Kalirin-7 (Kal-7) detected in the spinal dorsal horn via RT–PCR. (d) Unilateral microinjection of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) virus expressing Cre recombinase and EGFP into the mouse lumbar spinal dorsal horn (Scale bar, 300 μm). (e) Validation of Cre-mediated Kal-7 conditional knockout in mouse spinal dorsal horn (SDH-Kal-7−/− mice) by quantitative RT–PCR, showing 50% reduction of Kal-7, but not Kal-9 or Kal-12 isoforms, in total lysate from spinal L4-L5 segments, as compared with AAV-EGFP-injected Kal-7fl/fl mice (Kal-7fl/fl-EGFP control mice) (n=3 independent experiments). *P<0.05 as compared with control group; two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test. Error bars represent s.e.m.