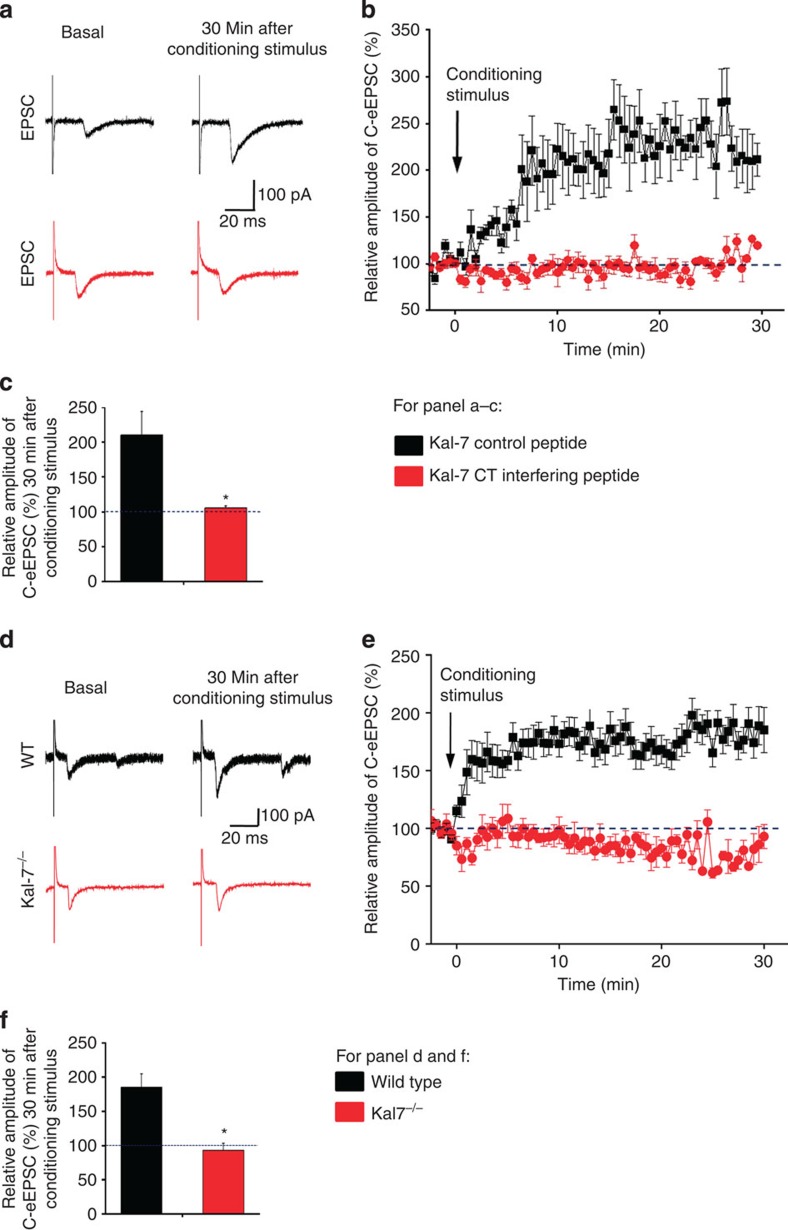
Figure 5. Functional impact of disrupting synaptic interactions of Kal-7 in spinal neurons or loss of Kal-7 expression on synaptic transmission.
(a–c) At synapses between C nociceptors and spinal projection neurons, intracellular application of a Kal-7 C-terminal (CT) interfering peptide, but not a control peptide, blocked spinal long-term potentiation (n=8–10 slices). (d–f) Analysis of synaptic long-term potentiation in spinal neurons of mice lacking Kal-7 (Kal-7−/− mice) and wild-type littermates (n=8–10 slices). Typical traces of evoked excitatory postsynaptic currents (eEPSCs) (a,d), time-course (b,e) and quantitative summary of % change in EPSC magnitude (c,f) are shown. *P<0.05 as compared with control group, Student's t-test. Error bars represent s.e.m.