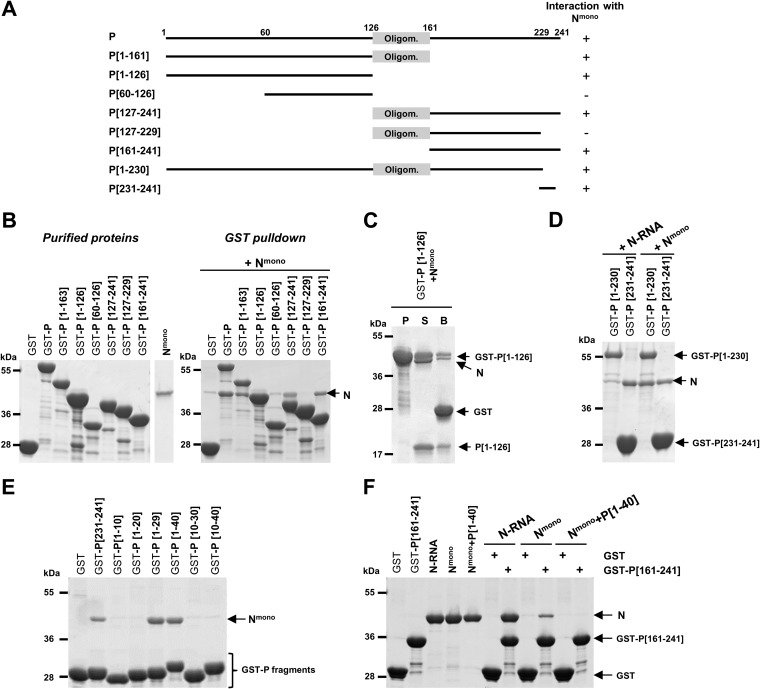
FIG 3.
Deletion mapping of Nmono binding domain(s) on P. (A) Schematic illustration of the wild-type and the truncated RSV P proteins used in this study. The oligomerization domain of P is represented as a gray box, and numbers indicate amino acid positions. Deletion mutants of P harboring a GST tag at the N terminus were purified on glutathione-Sepharose beads and incubated in the presence of Nmono. For each deletion mutant, the ability to interact with Nmono is summarized on the right. (B, C, D) GST-P-derived proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE before or after incubation with Nmono (B, C) or N-RNA rings (D), as indicated. (C) For GST-P[1-126], the presence of N0 after pulldown was verified after thrombin cleavage of GST tag (P, purification products; S and B, supernatant and beads after thrombin cleavage, respectively) (E, F) Identification of the minimal domain of P involved in the interaction with Nmono. (E) Analysis of copurification products of Nmono with P[231-241] and N-terminal fragments of P (GST-PΔ). (F) Study of the fixation of both N and C termini of P on Nmono. Recombinant N-RNA rings, Nmono, or P[1-40]+Nmono complex were incubated with GST or GST-P[161-241] bound to beads, and interactions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining.