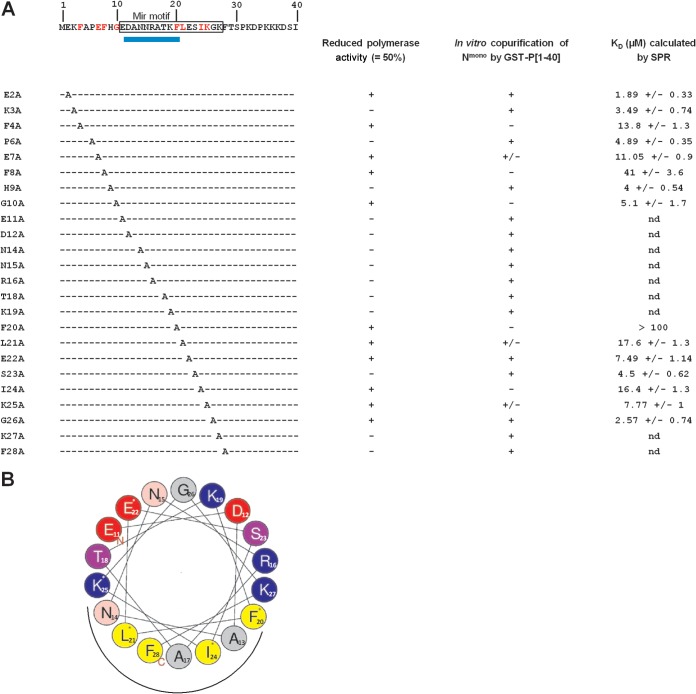
FIG 8.
Sequence of the N terminus of P and summary of effects of point mutations on RdRp activity and P-N0 interactions. (A) The sequence of the first 40 N-terminal residues of P is indicated at the top. Residues of the predicted mir motif are boxed. The location of the predicted α-helix is indicated by a blue rectangle below the sequence. The left-hand column indicates the point mutations. Right-hand columns summarize the impact of mutations on (i) the polymerase activity, (ii) in vitro copurification of GST-P[1-40] mutants with Nmono, and (iii) affinity of Nmono for GST-P[1-40] mutants; nd, not determined. Residues identified as critical for both polymerase and interaction with Nmono based on pulldown and SPR data are in red in the sequence. (B) Helical wheel representation (HeliQuest online program) of the putative α-helix located between residues 11 and 28 of P. Residues critical for N0-binding are indicated by a star, and the putative site of interaction with the Nmono is indicated by a black half-circle under the wheel. Positively charged residues are in blue, negatively charged residues in red, and hydrophobic residues in yellow.