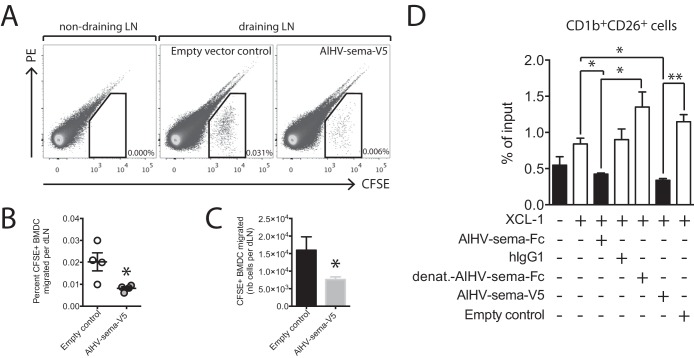
FIG 9.
AlHV-sema inhibits DC migration. (A to C) Bone marrow-derived DCs were differentiated from the femurs of a IIIEP/J male rabbit as described in Materials and Methods. BMDCs were matured overnight using E. coli LPS (2 μg/ml) before harvest and treatment with AlHV-sema-V5 (50 nM, 5 × 105 cells/ml) or empty vector control at 37°C during 3 h in bacterial petri dishes. Cells were then collected, counted, CFSE labeled, and injected in the footpads of IIIEP/J syngeneic male rabbits (2 × 106 cells in 0.5 ml per footpad), together with 5 μg of AlHV-sema-V5. Popliteal draining LNs and axillary nondraining LNs were harvested 2 days later, the cells were put into a single-cell suspension and counted, and the percentages of the migrated CFSE+ DCs were measured using flow cytometry (A). Dot plots show representative results for one rabbit. The percentages (B) and absolute numbers (C) of CFSE+ cells that migrated to the pLNs are plotted. The data are shown as means ± the SEM (n = 4). A Mann-Whitney unpaired t test was performed (*, P < 0.05). (D) Transwell migration assay on enriched sheep lymph subjected to recombinant mouse XCL-1 (100 ng/ml) and AlHV-sema (50 nM) treatment. Human IgG1, heat-denatured AlHV-sema-Fc, and empty vector supernatant were used as controls. Migrated cells were subjected to CD1b and CD26 double staining before flow cytometry analysis and the acquisition of 2,500 polystyrene microspheres. Migration is expressed as the percentage of input cells in the CD1b+ CD26+ gate. Bars show means ± the SEM of independent analyses in duplicates of three different sheep lymph samples. One-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post test was performed (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01).