FIG 3.
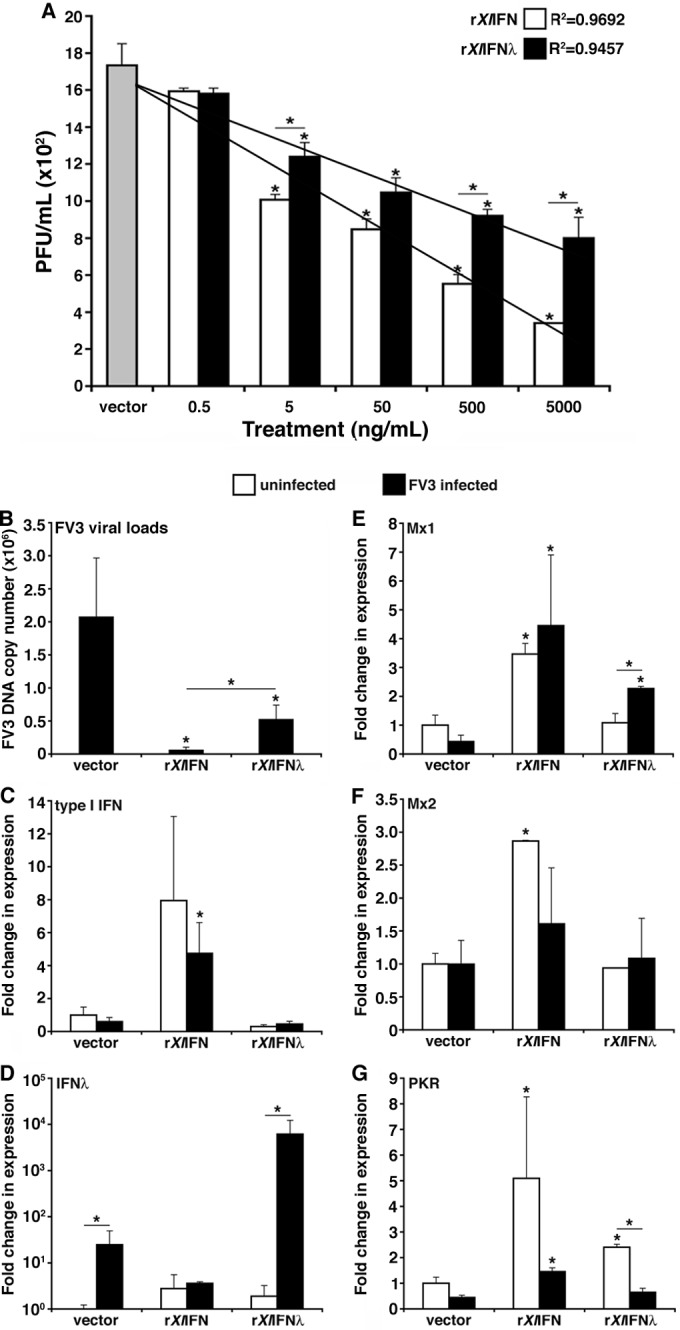
Assessment of the antiviral effects of rXlIFN and rXlIFN-λ on the kidney-derived A6 cell line. (A) A6 cells were pretreated for 6 h with 0.5, 5, 50, 500, or 5,000 ng/ml of either rXlIFN or rXlIFN-λ, infected with FV3 at an MOI of 0.5 for 16 h, and assessed for viral loads by plaque assays. (B to G) A6 cultures were treated with the vector control or 100 ng/ml of either rXlIFN or rXlIFN-λ for 6 h and infected with FV3 at an MOI of 0.5 for an additional 16 h. The FV3 DNA copy number was assessed by absolute qPCR against the FV3 vDNA Pol II (using a vDNA Pol II standard curve) (B). Antiviral qPCR gene expression analysis was performed for type I IFN (C), type III IFN (IFN-λ) (D), Mx1 (E), Mx2 (F), and PKR (G). Gene expression was analyzed relative to the level of the GAPDH endogenous control. Three A6 cell cultures were subjected to each of the experimental conditions (n = 3). Results are means ± standard errors of the means. Significant differences in the results relative to those with the vector control and between treatment groups (as denoted with a horizontal bar) are indicated (*, P < 0.05).
