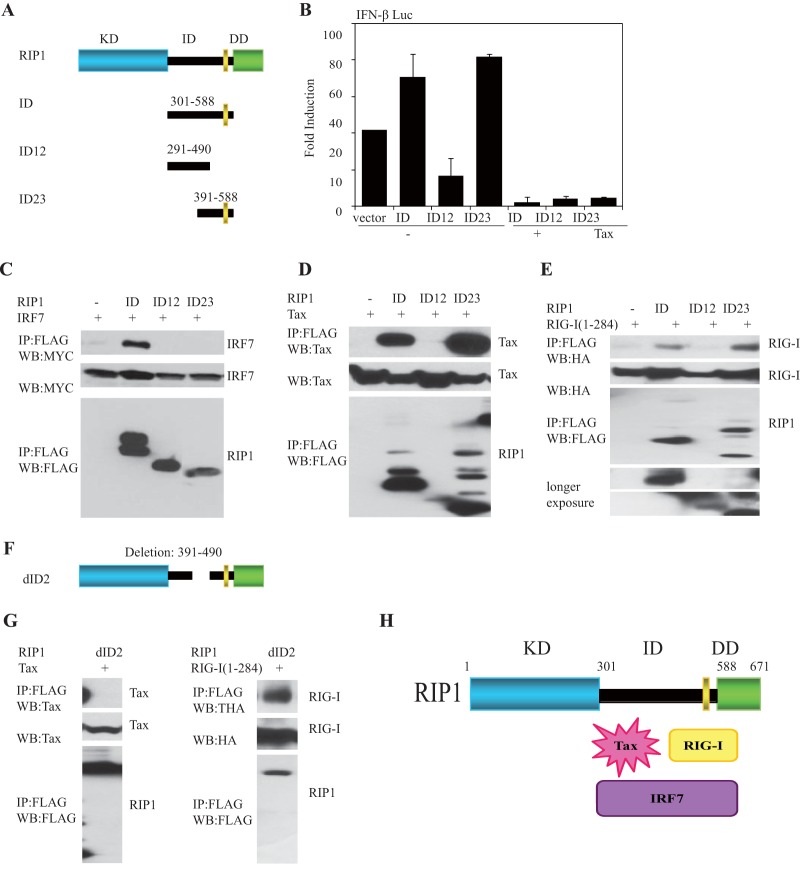
FIG 6.
Tax preferentially inhibits activity of IRF7. (A, B) Schematic figures of intermediate domain of RIP1 variants (A) and IFN-β-Luc (B) reporter assays examined in 293T cells using expression vector encoding FLAG-RIG-I(1-284), FLAG-RIP1 (ID, aa 301 to 588), FLAG RIP1(ID12, aa 291 to 490), or FLAG-RIP1(ID23, aa 391 to 588), either with or without Tax. (C, D, E) Co-IP analysis in 293T cells after expressing FLAG-RIP1 (ID, aa 301 to 588), FLAG-RIP1 (ID12, aa 291 to 490), or FLAG-RIP1(ID23, aa 391 to 588), and either Myc-IRF7, Tax, or HA-RIG-I (aa 1 to 284). Thirty-six hours later, cell lysates were immunoprecipitated, and IB analysis was performed with the indicated antibodies. (F) Structure of dID2 (deletion, aa 391 to 490) of RIP1. (G) Co-IP assay revealed that intermediate domain aa 391 to 490 of RIP1 was essential for Tax association to RIP1 but not for HA-RIG-I(1-284). 293T cells were transfected with ID2 of FLAG-RIP1 (deletion, aa 391 to 490), and either Tax or HA-RIG-I(1-284) for 36 h. The lysates were pulled down with anti-FLAG antibody, and IB was performed with anti-Tax antibody. (H) Schematic model of RIP1-interacting proteins and Tax. Error bars, ±SD.