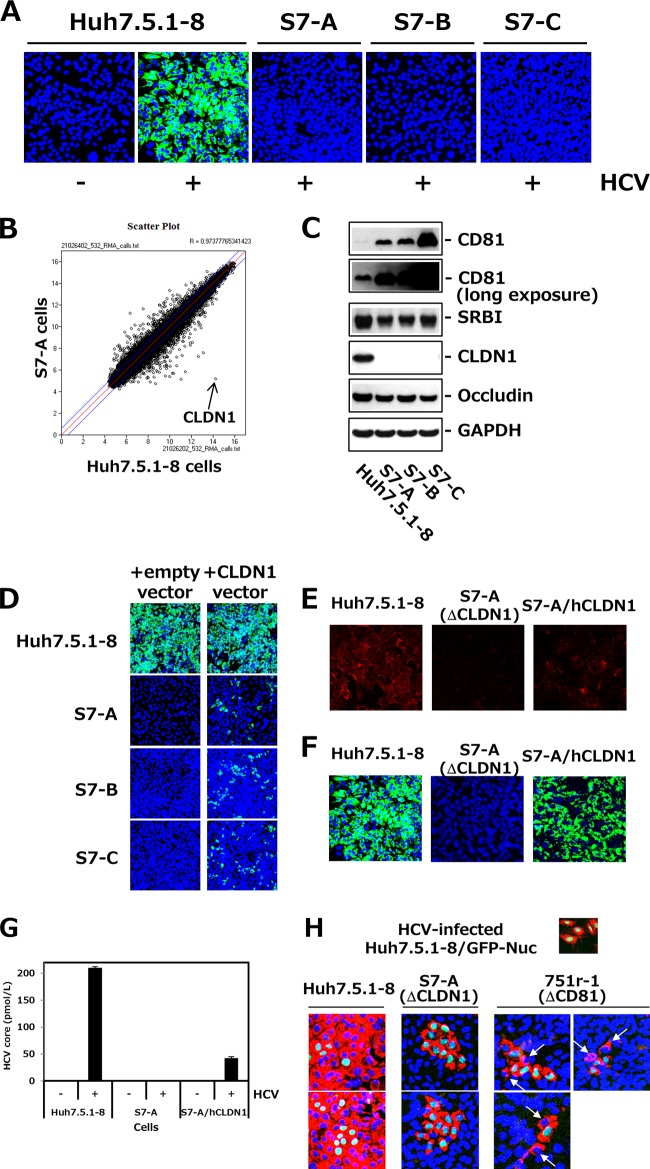
FIG 2.
Isolation and characterization of Huh7.5.1-derived CLDN1-defective clones. (A) Huh7.5.1-derived cell clones, i.e., S7-A, -B, and -C, and control Huh7.5.1-8 cells were infected with HCVcc. At 3 dpi, cells were stained with anti-HCV core protein (green) and DAPI (blue). (B) Scatterplot showing the results of the RNA microarray experiments (Huh7.5.1-8 versus S7-A cells). Each data point represents a single gene. The arrow indicates CLDN1. (C) Each cell lysate was subjected to immunoblotting to detect CD81, SRBI, CLDN1, occludin, and GAPDH. (D) Each cell was transfected with pcDNA3.1/Hygro (empty vector) or pcDNA3.1/Hygro-hCLDN1 (CLDN1 vector). After 2 days, transfected cells were infected with HCVcc and stained with anti-HCV core protein (green) and DAPI (blue) at 3 dpi. The transfection efficiency was usually ∼30% when we observed it 2 days after transfection. (E) Huh7.5.1-8 cells, S7-A cells, and S7-A cells that stably expressed human CLDN1 (S7-A/hCLDN1) were stained with anti-CLDN1 pAb (red) and observed by confocal fluorescence microscopy. (F) Each cell culture was infected with HCVcc and stained with anti-HCV core protein (green) and DAPI (blue) at 3.5 dpi. (G) HCV core contents in the culture supernatants from the different cell types were quantitated by ELISA at 3.5 dpi. (H) Huh7.5.1-8/GFP-Nuc cells with green nuclear staining were infected with HCVcc and cultured for 1.5 days. HCV-infected Huh7.5.1-8/GFP-Nuc cells were mixed with naive Huh7.5.1-8, S7-A, or 751r-1 cells, at a cell number ratio of 1:10 in each case, and plated onto a 24-well plate. After 5.5 days, cells were stained with anti-HCV core protein (red) and DAPI (blue). Arrows indicate HCV-infected 751r-1 cells.