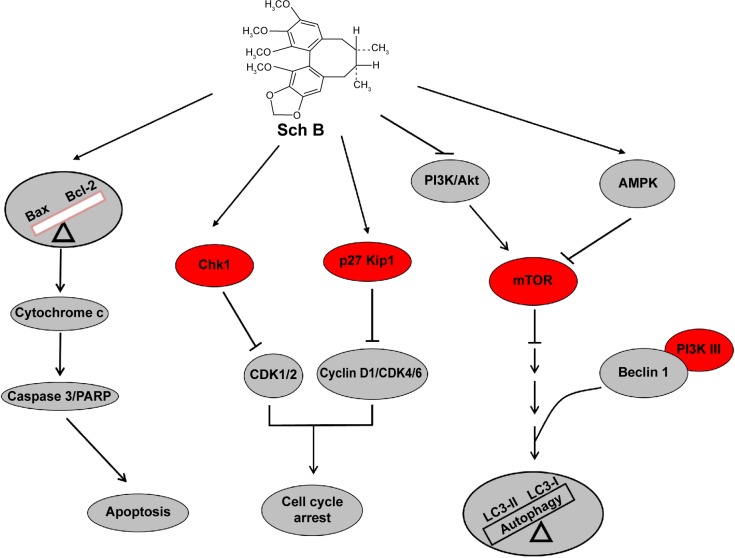
Figure 12.
Proposed mechanisms for the cytotoxic effects of Sch B on mouse AML-12 and RAW 264.7 cells.
Notes: Sch B induces cell cycle arrest with up-regulation of the expression level of p27 Kip1 and Chk1, and down-regulation of the expression level of cyclin D1 and CDK2. Furthermore, Sch B induces the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria to cytosol, which promotes cleavage of caspase 3 and PARP, and leads to apoptosis. In addition, Sch B induces remarkable autophagy with the involvement of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in AML-12 and RAW 264.7 cells. The red ovals indicate key downstream targets of Sch B. The triangle means the balance of two key proteins.
Abbreviations: p, phosphorylated; Sch B, schisandrin B; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt, protein kinase B; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; AMPK, 5′-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; LC3-I, cytosolic microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3; LC3-II, LC3-phosphatidylethanolamine conjugate; CDK, cyclin-dependent kinase; Chk1, checkpoint kinase 1; PARP, poly-adenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; Bax, Bcl-2-like protein 4/Bcl-2-associated X protein.