FIG 3.
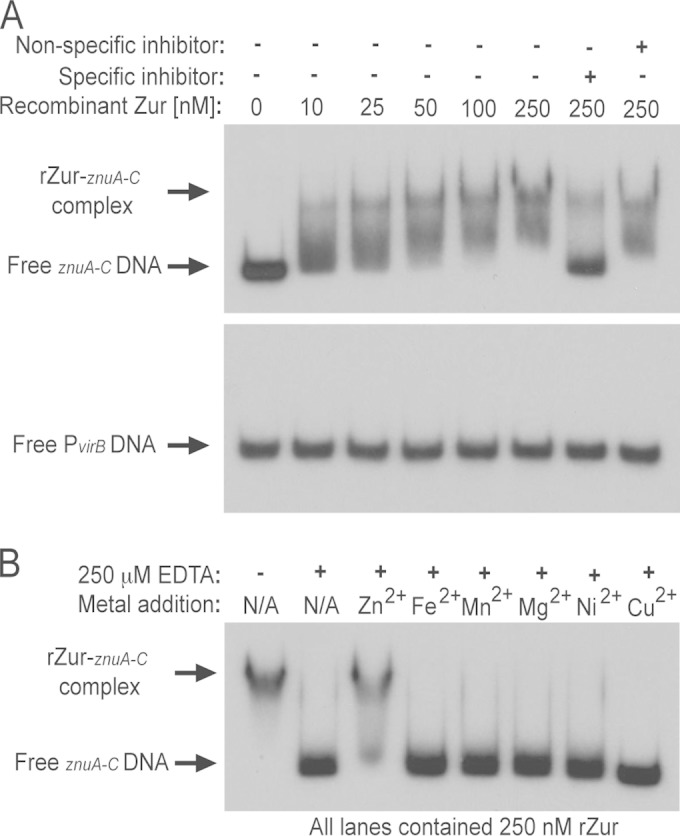
Zur binds directly to the znu (zinc uptake) promoter regions and requires zinc for interactions with DNA. (A) Recombinant Zur (rZur) protein was assessed for binding to the znuA-znuC intergenic region using electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs). Increasing concentrations of rZur were incubated with radiolabeled znuA-znuC intergenic region DNA, and in some binding reactions, unlabeled specific (znuA-znuC intergenic region DNA) or nonspecific (zntA-zntR intergenic region DNA) competitor DNA fragments were included as controls. The presence (+) and absence (−) of components in the binding reaction mixture are indicated. In addition to testing the binding of rZur to the znuA-znuC intergenic region, interactions between rZur and DNA corresponding to the virB promoter were also assessed as a negative control. (B) EMSAs performed with the znuA-znuC intergenic region DNA and rZur protein in the presence of EDTA and various divalent metal cations. All binding reaction mixtures contained 250 nM rZur and 50 μM ZnCl2, and, where indicated, 250 μM EDTA was included in some samples. To assess the metal specificity of rZur binding to DNA, an additional divalent metal cation (Zn2+, Fe2+, Mn2+, Ni2+, or Cu2+) was added to the binding reaction mixtures at a final concentration of 25 μM in the presence of EDTA.
