Table 2.
Spectral, kinetic and energetic properties of N-methoxy and N-ethylheterocycle excited triplet states in acetonitrile at room temperature.
| Structure* | 3λ*max† (nm) | 3kq*(O2)‡ (M−1 s−1) | 3E*0,0§ (kcal mol−1) | Ered|| (V vs. SCE) | 3Ered*¶(V vs. SCE) | 3t*# (ns) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
6 | 700 | 6.2 × 108 | 67.2 | −0.53 | 2.4 | 80 |

|
6E | 700 | 7.8 × 108 | 67.2 | −0.67** | 2.2 | 50 |

|
7 | 550 | 1.1 × 109 | 56.5 | −0.65 | 1.8 | 600 |

|
7E | 550 | 1.0 × 109 | 56.5 | −0.79 | 1.7 | 500 |
|
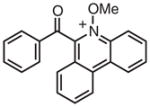
8 | 525 | 1.8 × 109 | 57.2 | −0.63 | 1.9 | 400 |

|
8E | 525 | 1.2 × 109 | 58.1 | −0.77 | 1.7 | 400 |

|
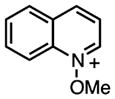
3E | 500 | 4.5 × 108 | 60.3 | −0.96†† | 1.7 | 1000 |
|
1 | 440 (500)‡‡ | 5.3 × 108 | – | −0.84 | – | 2700 |
|
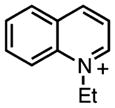
1E§§ | (440) 500‡‡ | 6.0 × 108 | 60.4§§ | −0.98|||| | 1.6 | 1900 |
Experiments performed using tetrafluoroborate or hexafluorophosphate salts except where noted;
Absorption maximum of the excited triplet state;
Bimolecular rate constant for quenching of the excited triplet by oxygen;
Energy of the 0,0 phosphorescence transition measured in EPA or ethanol/methanol/methyl iodide glass at 77 K;
Estimated reduction potential of the N-methoxy or N-ethylheterocycle versus SCE, from measurements as part of this work or as indicated. The reduction potentials of the N-methoxy structures were not measured but are obtained by adding 0.15 V to those for the corresponding N-ethyl structure, as described in Ref. (37);
Reduction potential of the excited triplet state estimated as Ered* = Ered + (3E*0,0/23.06);
Measured lifetime of the excited triplet state;
from Ref. (64);
from Ref. (65);
Two maxima observed, the weaker absorbance is in parenthesis;
Iodide salt;
From Ref. (66).
