Figure 2.
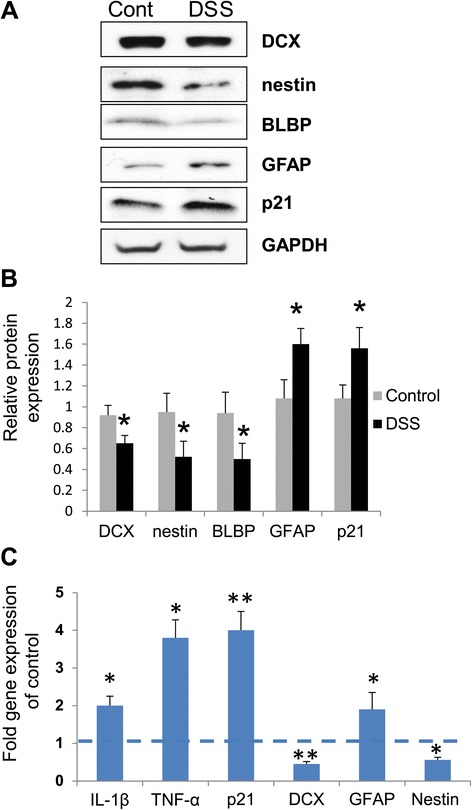
Chronic intestinal inflammation negatively affects hippocampal neurogenesis. Mice were sacrificed on day 29 after the beginning of DSS treatment. (A) Western blot analysis of markers of neurogenesis and p21. Three independent experiments were performed, and representative blots are shown depicting pooled samples derived from DSS-treated and control mice; (B) intensities of protein bands were quantified from nine individual samples run together, normalized to GAPDH and presented as a fold change relative to control animals; (C) mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines, markers of neurogenesis, and p21 in the hippocampus of DSS-treated mice. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. All samples from three experiments (n = 9) were run together in triplicates and normalized against GAPDH. Results are expressed in fold change vs. control taken as 1 (broken line); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. BLBP, brain lipid binding protein; Cont, control; DCX, doublecortin; DSS, dextran sodium sulfate; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein.
