Figure 1.
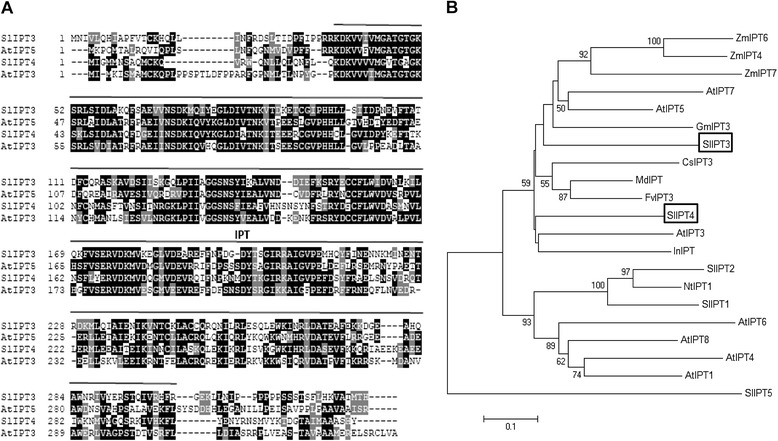
Identification of SlIPT3 and SlIPT4. (A) Full-length protein sequence alignment of SlIPT3, SlIPT4 and Arabidopsis AtIPT3 and AtIPT5. Identical residues are colored in black and conserved residues in dark gray. The isopentenyltransferase (IPT) domain is labeled. (B) Phylogenetic relationships between SlIPT3 [ADZ28498], SlIPT4 [AEE39459] and related proteins of Cucumis sativus CsIPT3 [XP_004136062], Ipomoea nil InIPT [BAG55006], Malus domestica MdIPT [ADY80558], Fragaria vesca FvIPT3 [XP_004290672], Arabidopsis thaliana AtIPT3 [Q93WC9], AtIPT4 [Q9SB60], AtIPT5 [Q94ID2], AtIPT6 [Q9C6L1], AtIPT7 [Q94ID1] and AtIPT8 [Q9LJL4], Glycine max GmIPT3 [XP_003528670], Zea mays ZmIPT4 [ABY78883], ZmIPT6 [ABY78885] and ZmIPT7 [ABY78886], Solanum lycopersicum SlIPT1 [BAM08995], SlIPT2 [BAM08996], SlIPT5 [BAM08998] and SlIPT6 [XP_004251888], Nicotiana tabacum NtIPT1 [AFV15392]. The phylogenetic tree was constructed according to the neighbor-joining method, using MEGA5 [27]. The percentage of reliability of each branch point of the rooted tree, as assessed by the analysis of 1000 trees (bootstrap replicates), is shown on the branch stem.
