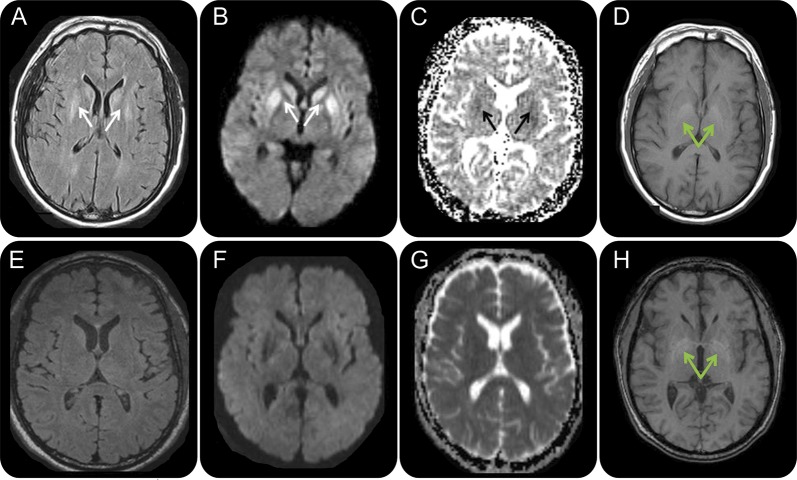
Figure 1. Serial brain MRIs in case 1, a 50-year-old man with extrapontine myelinolysis.
FLAIR (A, E), DWI (B, F), ADC map (C, G), and T1 (D, H) sequences, in radiologic orientation, 2 months (A–D) and 3 months (E–H) after onset. Initial MRI 2 months after onset (A–D) shows symmetric bilateral striatal FLAIR/DWI hyperintensities (A, B; solid white arrows) with corresponding hypointensities on the ADC map suggesting restricted diffusion (C; solid black arrows). Bilateral globus pallidus hyperintensities were present on T1-weighted imaging (D; green arrows). MRI 1 month later (E–H), 3 months after onset, shows resolution of the prior FLAIR, DWI, and ADC map abnormalities but no change in the globus pallidus T1 hyperintensities (H; green arrows). ADC = apparent diffusion coefficient, DWI = diffusion-weighted imaging; FLAIR = fluid-attenuated inversion recovery.