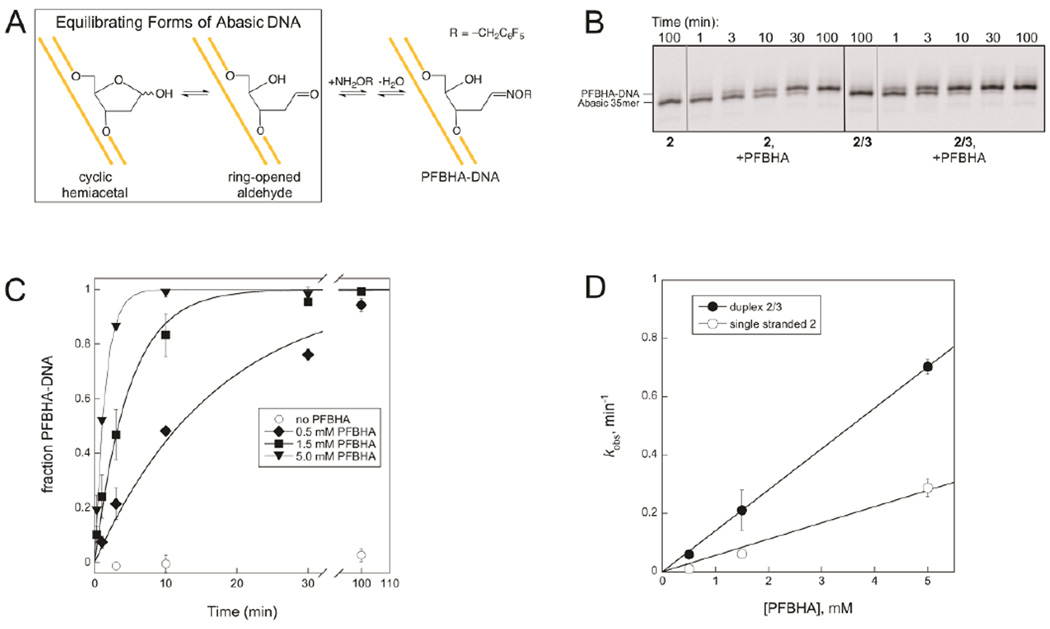
Figure 7.
Reaction of PFBHA and abasic DNA. A. The oxyamine adduct PFBHA-DNA is the product of the reaction between PFBHA and abasic DNA. This reaction is analogous to the well-characterized reaction of methoxyamine with abasic DNA48–50 but has the advantage that the larger PFBHA adduct is more easily separated from the abasic DNA substrate on a gel. B. PFBHA reacts with 2 or 2/3 to form PFBHA-DNA. No adduct forms in the absence of PFBHA. Reactions contained 0.25 µM DNA and were carried out at 37 °C and pH 6.5 with or without 1.5 mM PFBHA. Samples were reduced with NaBH4 before separation on a 20% denaturing polyacrylamide gel. This image displays only the region of the gel where the 35mer and the PFBHA-35mer appear; A full image of the same gel (Figure S3) shows that ICL formation is minimal in reactions of duplex 2/3 when PFBHA is present, because PFBHA outcompetes the exocyclic amine for reaction with the abasic site at the concentrations of PFBHA used. C. The kobs for formation of PFBHA-DNA increases with PFBHA concentration in duplex 2/3 reactions. Values of kobs at each PFBHA concentration were determined from exponential fits to the data and are plotted in D. D. Linear fits for the dependence of kobs on PFBHA concentration give second order rate constants for the reaction of PFBHA with 2 of 0.06 mM−1min−1 and with 2/3 of 0.14 mM−1min−1.