Figure 1. (a) Diagram of AKT/mTOR and MDM2/p53 signalling crosstalk in GBM and in GSCs.
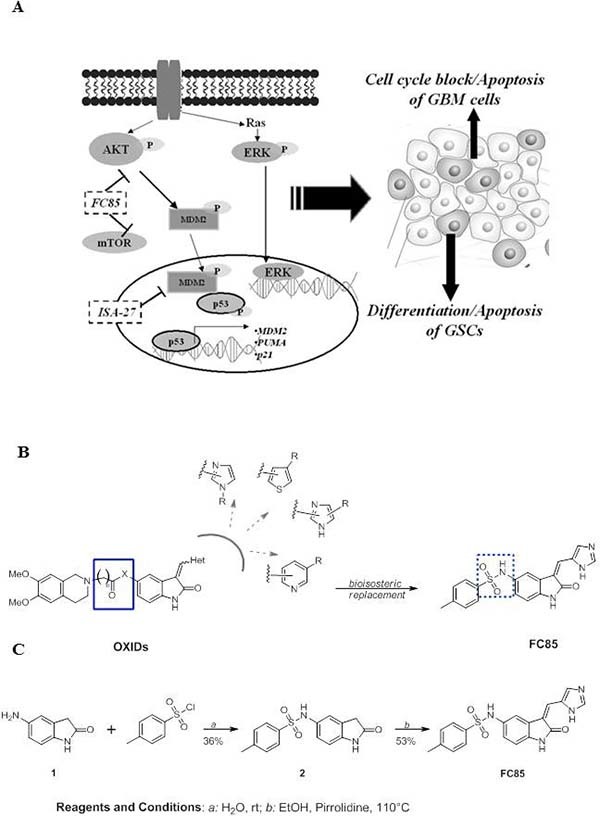
AKT/mTOR deactivation decreases MDM2 and p53 phosphorylation and increases stable p53, which triggers its downstream targets. Simultaneously, p53 may increase PTEN to suppress AKT activation further. FC85 inhibited both AKT (Ser473) and mTOR (Ser2448) phosphorylation. ISA27 dissociated the MDM2-p53 complex, thus re-activating p53. The combined therapy with FC85+ISA27 more efficiently re-activated the p53 pathway, producing a synergic effect on the inhibition of GBM cell viability; most importantly, the simultaneous inhibition of AKT/mTOR and of the MDM2-p53 complex led to a synergic effect in triggering cellular differentiation/apoptosis of GSC subpopulation. (b) The design of FC85 starting from the general structure of OXIDs. (c) The synthetic procedure for the preparation of FC85.
