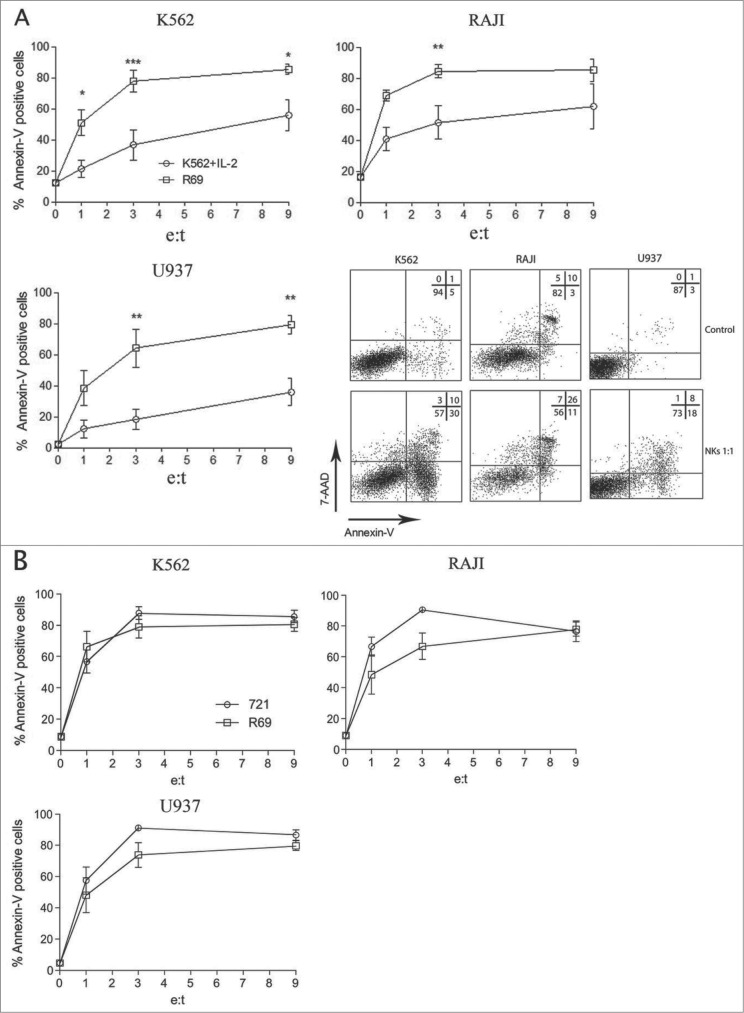
Figure 1.
(See previous page) Human NK cells activated with R69-LCLs present higher cytotoxicity against haematological cancer cellsthan those activated with K562 cells plus IL2. Natural killer (NK) cells were enriched by magnetic isolation (MACS) from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and activated over the course of 5 days with K562 cells plus interleukin 2 (IL2) (A) or Epstein-Barr virus positive lymphoblastoid B cells (R69-LCLs) (A, B) or HLA-I deficient EBV+-LCL 721.221 LCLs (B). Subsequently, activated NK cells were incubated with K562, Raji and U937 cells at different effector/target (E:T) cell ratios for 4 hours. Phosphatidyl serine plasma membrane externalization (Annexin-V) and membrane permeabilization (7-aminoactinomycin D [7AAD]) were analyzed by 3-color fluorescence cytometry as described in Materials and Methods. A representative experiment is shown in dot plots using NK cells stimulated with K562/IL2 at 1:1 E:T cell ratio. Numbers correspond to the percentage of cells in each quadrant. Results are presented as the mean±SEM of 5 independent donors from 2 independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni´s post hoc test; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.