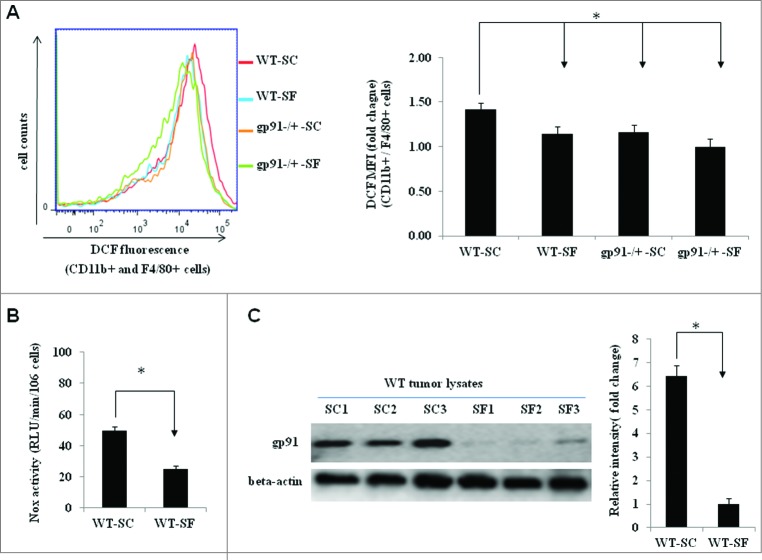
Figure 2.
SF reduces reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) as well as gp91phox downregulation in expression and activity. (A) Flow cytometric analysis showed reduced levels of ROS in TAMs isolated from TC1 tumor-bearing gp91phox-/Y-SC (n = 12), gp91phox-/Y-SF (n = 18) and WT-SF (n = 18) mice compared with WT-SC (n = 13) mice. Left panel, a representative flow cytometric histogram of DCF-positive cells (gated on cells expressing CD11b and F4/80). Right panel, ROS levels were quantified as the median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of DCF-positive cells among CD11b+ and F4/80+ cells. Data are plotted as fold changes18 compared with WT-SC. *p< 0.05. (B) Summary of Nox enzymatic activity experiments in TAMs isolated from wild type mice exposed to SC (n = 6) or SF (n = 6) illustrating significant reductions in Nox activity in tumors from mice exposed to SF conditions (*p < 0.05 vs. SC). (C) Immunoblots of tumor lysates revealed marked reduction in gp91phox protein expression in WT-SF tumors (n = 3) when compared with WT-SC (n = 3) (left panel). Band intensities were quantified and data are expressed as fold changes over β-actin (right panel). *p < 0.05.