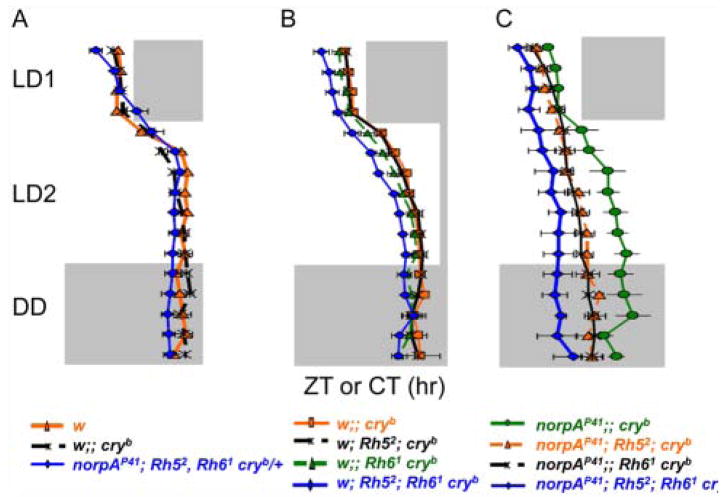
Figure 3.
Direct comparison of evening activity phase during shifted LD cycles. Evening activity peak phase of related genotypes was plotted to allow comparison of the resynchronization kinetics. (A) Comparison of w; cryb and norpAP41; Rh52; Rh61 cryb/+ flies, showing quick resynchronization of cry+ compared to homozygous cryb genotypes. (B) Comparison of single and double Rh52 and Rh61 mutants combined with cryb compared to cryb single mutants, showing that the 2 Rhodopsin mutants combined slow down resynchronization. (C) Comparison of the same genotypes as shown in the middle panel, additionally carrying norpAP41. Rh52 and Rh61 further slow down resynchronization of norpAP41; cryb double mutants, demonstrating their norpA-independent function. n corresponds to those indicated in Figures 2 and 4. Gray or black areas indicate darkness, and white areas indicate lights-on.