Figure 1.
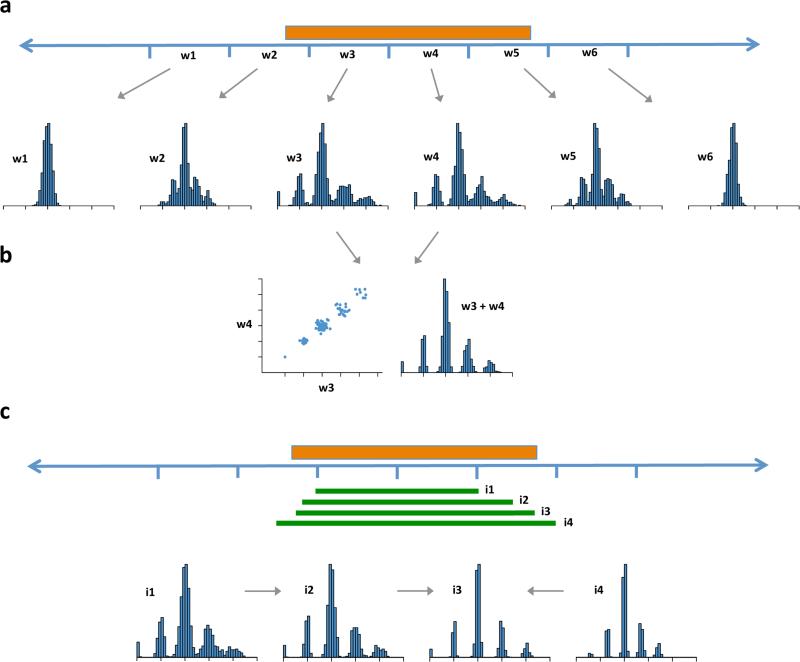
Ascertainment of multi-allelic copy number variations (mCNVs) across the human genome. Multi-modal patterns of variation for a high-frequency CNV (orange box represents the true extent of the CNV) can be detected in multiple windows (w1 – w6) that overlap the CNV segment (a). Where read-depth distributions from adjacent windows are highly correlated across many genomes, these windows are merged to increase power for genotyping (b). To more precisely estimate the genome sequence affected (c) many candidate intervals (green bars, i1 – i4) are tested; intervals for which the data most strongly coalesce to integer genotypes with high posterior likelihoods define the estimated CNV boundaries (i3).