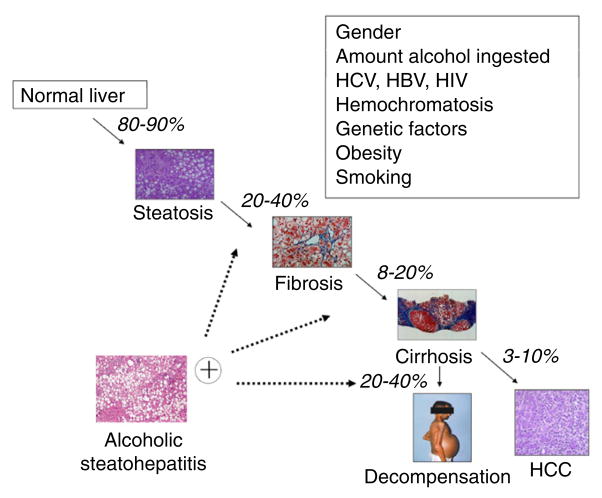
Figure 1.
Natural history of alcoholic liver disease and modifier factors. More than 80–90% of heavy drinkers develop fatty liver, but only up to 20–40% of this population develops more severe forms of alcoholic liver disease (ALD), including fibrosis, alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocarcinoma (HCC). Multiple other risk factors have been proposed to play a role in susceptibility to severe forms of ALD. HBV, hepatitis B virus; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus.