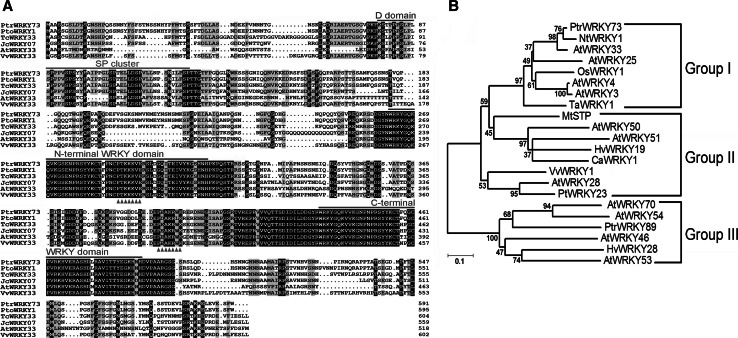
Fig. 2.
Alignment and phylogenetic analysis of PtrWRKY73 with other WRKY amino acid sequences. a Sequence alignment PtrWRKY73 and the other WRKYs. Sequences were from [(P. tomentosa × P. bolleana) × P. tomentosa] (PtoWRKY1), Theobroma cacao (TcWRKY33), J. curcas (JcWRKY07), V. vinifera (VvWRKY33) and A. thaliana (ATWRKY33). Identical amino acids were indicated by white letters on a black background and conservative amino acids by black on a dark gray background. The N-terminal and C-terminal WRKY domains were highlighted by green lines. D domain and SP cluster are highlighted by blue and red lines, respectively. The putative nuclear localization signals (NLS) were predicted and pointed out by the orange triangles at the bottom. b Phylogenetic relationships of PtrWRKY73 proteins from P. trichocarpa and selected species. Sequences were from N. tabacum (NtWRKY1), N. attenuate (NaWRKY3), Hordeum vulgare (HvWRKY19, HvWRKY28), V. vinifera (VvWRKY1), P. tremula x P. Alba (PtWRKY23), Medicago truncatula (MtSTP), Oryza sativa (OsWRKY1), Triticum aestivum (TaWRKY1), Capsicum annuum (CaWRKY1), P. trichocarpa (PtrWRKY89), A. thaliana (AtWRKY3, AtWRKY4, ATWRKY25, AtWRKY28, ATWRKY33, AtWRKY46, AtWRKY50, AtWRKY51, AtWRKY53, ATWRKY54, ATWRKY70). And the accession numbers were described in Supplementary Table 1 (color figure online)