Figure 2.
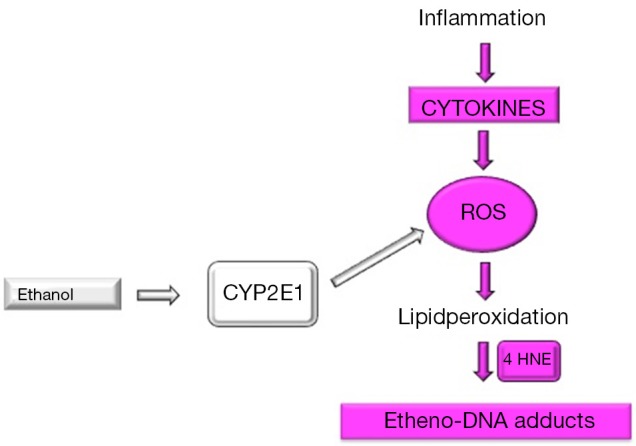
Simplified pathophysiology of ROS and etheno-DNA adduct formation. In NASH, inflammation driven cytokine secretion results in ROS generation, which leads to lipidperoxidation with the occurrence of lipidperoxidation products such as 4 HNE. These adducts react with DNA bases to form exocyclic etheno-DNA adducts. Chronic alcohol consumption results in the induction of CYP2E1, which is involved in ethanol oxidation through the microsomal ethanol oxidizing pathway. During this reaction ROS is generated without inflammation. ROS, reactive oxygen species; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; 4 HNE, 4-hydroxynonenal; CYP2E1, cytochrome P450 2E1.
