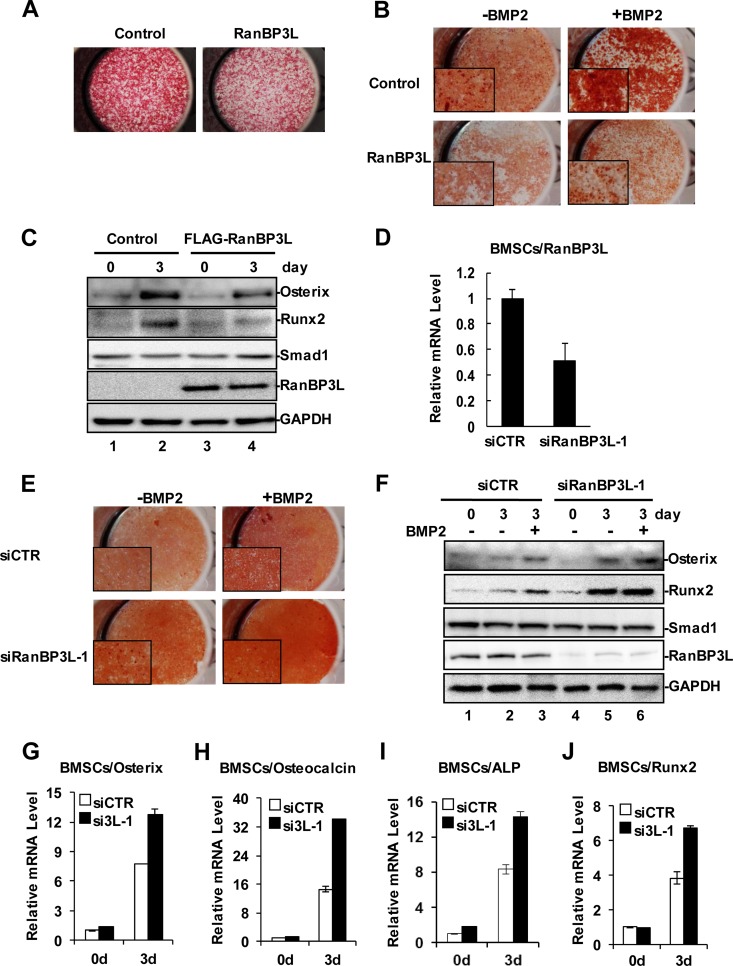
FIG 3.
RanBP3L blocks BMP-induced osteogenesis in BMSCs. (A) Overexpression of RanBP3L reduces ALP production in mouse BMSCs. Pools of BMSCs with stably expressing RanBP3L were achieved by lentivirus infection. (B) Overexpression of RanBP3L reduces bone formation in mouse BMSCs. RanBP3L-OE stable cells and control cells were treated with BMP2 (50 ng/ml) for 14 days or not treated. Alizarin red staining was measured as described in Materials and Methods. (C) Overexpression of RanBP3L decreases BMP-promoted osteogenic differentiation in mouse BMSCs. RanBP3L-OE stable cells and control cells were treated with BMP2 (50 ng/ml) for 3 days or not treated. Cells were harvested, and Western blotting was conducted with the indicated antibodies. (D) Knockdown of RanBP3L enhances BMP2-induced ALP activity in BMSCs. BMSCs were transfected with the indicated siRNAs and cultured in osteogenic differentiation medium with or without BMP2 (50 ng/ml). ALP activity was detected as described in the legend to Fig. 2A. (E) Knockdown of RanBP3L enhances BMP2-induced bone formation in mouse BMSCs. BMSCs were transfected with the indicated siRNAs and treated with BMP2 for 9 days to induce osteogenic differentiation or not treated. Alizarin red staining was done as described above for panel B. (F) Depletion of RanBP3L increases BMP-induced osteoblast maturation in mouse BMSCs. BMSCs were transfected with the indicated siRNAs and then treated with BMP2 (50 ng/ml) for 3 days. The osteoblast markers were detected by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (G to J) Knockdown of RanBP3L enhances Runx2 (G), Osterix (H), osteocalcin (I), and ALP (J) expression. BMSCs were transfected with the indicated siRNAs, and isolated RNAs were subjected to qRT-PCR analysis as described in the legend to Fig. 1G.