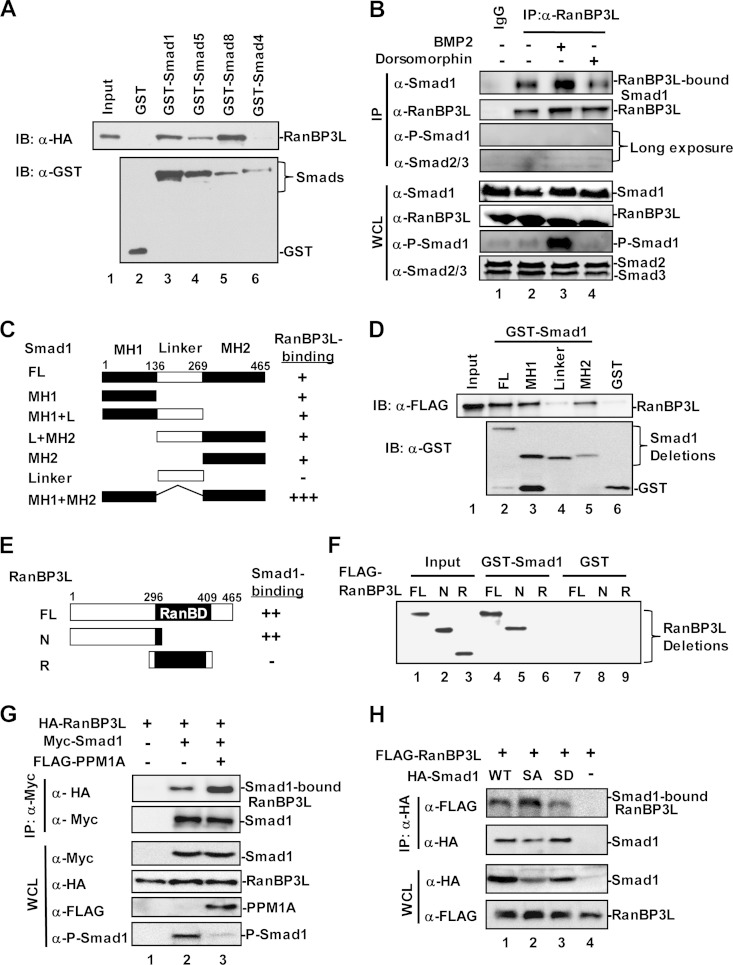
FIG 5.
RanBP3L physically interacts with Smad1/5/8. (A) RanBP3L directly binds to Smad1, -5, and -8 but not Smad4 in vitro. In vitro binding was carried out with purified GST-tagged Smads and in vitro-translated RanBP3L. IB, immunoblot. (B) RanBP3L interacts with Smad1 in vivo. C2C12 cells were treated with BMP2 or dorsomorphin for 2 h. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-RanBP3L antibody or control IgG antibody. The immunocomplexes and input were analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (C and D) RanBP3L binds to both the MH1 and MH2 domains of Smad1. In vitro binding assays were carried out as described above for panel A. FL, full length. (E and F) Smad1 binds to the N terminus of RanBP3L. Experiments were performed as described above for panel A. (G) PPM1A enhances the interaction between RanBP3L and Smad1. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. Levels of these proteins in IP products and whole-cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting. (H) RanBP3L has a higher binding affinity for the dephosphorylated form of Smad1. HEK293T cells were cotransfected with HA-RanBP3L, together with FLAG-Smad1 or its mutations (Smad1-2SA [unphosphorylated form] or Smad1-2SD [phosphorylation-mimicking form]). Levels of these proteins in IP products and whole-cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting.