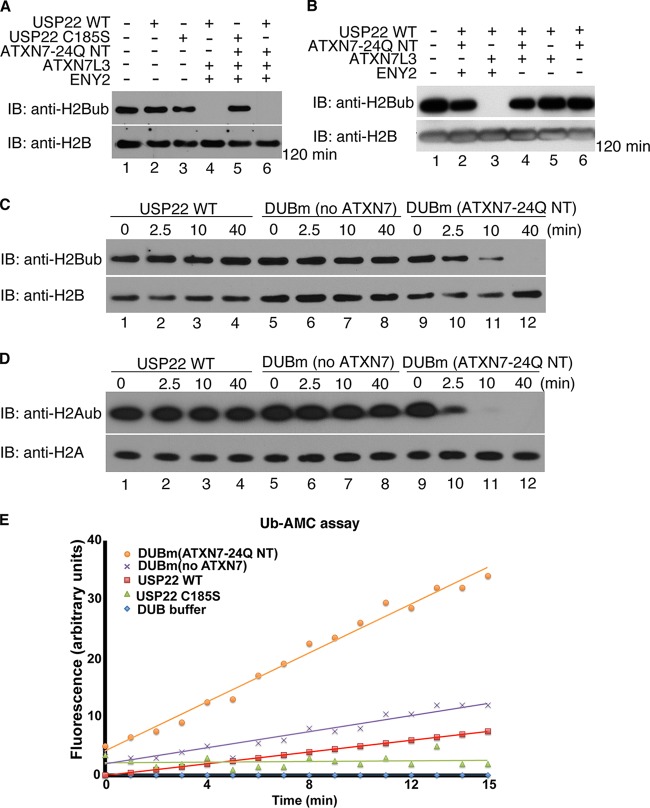
FIG 2.
ATXN7-24Q NT promotes robust DUB activity of the DUBm in vitro. (A) In vitro deubiquitination assays using core histones as the substrates were performed with USP22 alone (lanes 2 and 3), trimeric DUBm (no ATXN7-24Q NT; lane 4), and tetrameric DUBm (with ATXN7-24Q NT, lanes 5 and 6). The USP22 C185S catalytically inactive mutant served as a negative control (lanes 3 and 5). The trimeric and tetrameric complexes had similar activities on ubiquitinated H2B after 2 h. (B) In vitro DUB assays using core histones were performed for different combinations of DUBm subunits coinfected in Sf21 insect cells, in order to test potential enzymatic activity. Similar amounts of USP22 in these complexes were incubated with core histones for 2 h. No activity was observed in any dimeric complex (lanes 5 and 6), and the only trimeric complex with obvious enzymatic activity contained USP22, ATXN7L3, and ENY2 (lane 3). (C and D) In vitro DUB assays using core histones were performed with USP22 alone (lanes 1 to 4), DUBm (no ATXN7-24Q NT; lanes 5 to 8), and DUBm (with ATXN7-24Q NT; lanes 9 to 12), and samples were collected for analysis at the indicated time points. H2A (D) and H2B (C) ubiquitination was monitored with antibodies specific for these modifications. In all assays (A to D), core histones were purified from HEK293T cells. (E) Hydrolysis of ubiquitin-AMC (0.5 μM) alone or with similar amounts of recombinant USP22, DUBm (no ATXN7-24Q NT), and DUBm (with ATXN7-24Q NT). The release of AMC fluorescence was monitored by a spectrophotometer at 528 nm. The tetrameric DUBm with ATXN7-24Q NT showed the highest enzymatic activity. The USP22 WT or catalytic mutant was tagged with HA; ATXN7-24Q NT, ATXN7L3, and ENY2 were all tagged with Flag.