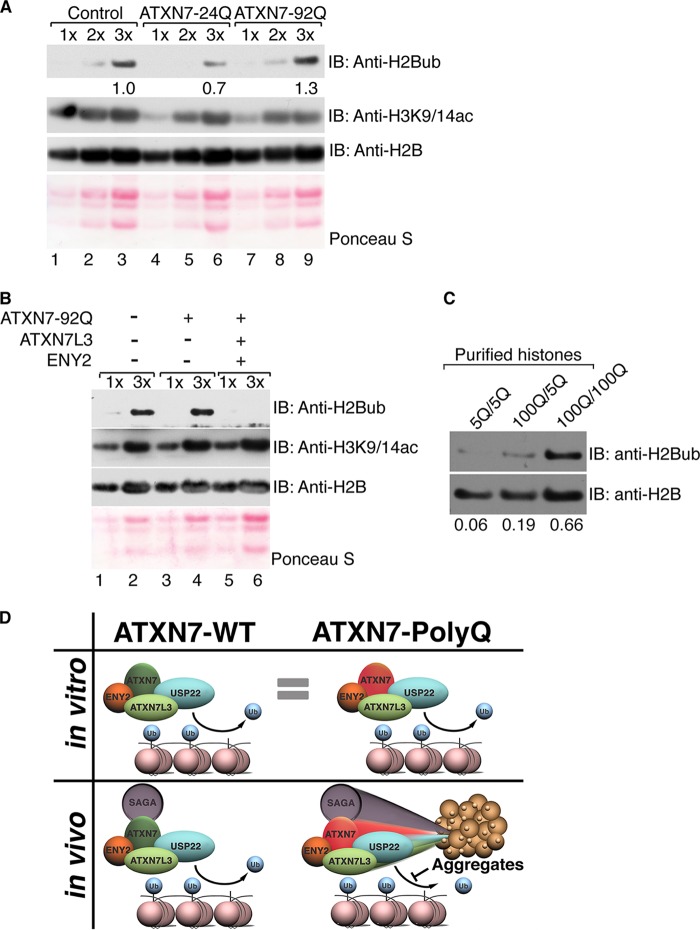
FIG 5.
Solubility of ATXN7-92Q in vivo correlates with DUB activity. (A) Core histones were purified from human astrocytes infected with empty vector (lanes 1 to 3), ATXN7-24Q (lanes 4 to 6), or ATXN7-92Q (lanes 7 to 9) and were analyzed by electrophoresis of increasing sample amounts (1× to 3×), and the levels of H2Bub were monitored with antibodies specific for this modification. The levels of H2B ubiquitination increased in astrocytes expressing ATXN7-92Q, indicating impaired deubiquitination. Quantification of H2Bub levels was normalized to H2B levels using ImageJ software. (B) Cooverexpression of ATXN7L3 and ENY2 enhances global H2Bub deubiquitination in astrocytes expressing ATXN7-92Q, whereas H3K9/14ac levels are not altered. Different sample amounts (1× and 3×) were analyzed. H2B immunostaining or Ponceau S staining served as a loading control. (C) Core histones were purified from the cerebellums of 4-month-old mice bearing wild-type (5Q) or mutant (100Q) alleles of the ATXN7 gene. Both ATXN7100Q/100Q and ATXN7100Q/5Q mice exhibit SCA7 symptoms over time, but disease progression in ATXN7100Q/100Q mice was faster and more severe than that in ATXN7100Q/5Q mice. Immunoblot analysis was used to detect H2Bub levels with anti-H2Bub antibody. Samples from both ATXN7100Q/100Q and ATXN7100Q/5Q mice show increased H2B ubiquitination, with the effect being more severe in the samples from ATXN7100Q/100Q mice. H2Bub levels were normalized to H2B levels using ImageJ software. Representative results chosen from more than three independent experiments are shown. (D) Model of the contribution of ATXN7-poly(Q) to SCA7 disease in humans. In vitro, soluble DUBm with ATXN7-92Q exhibits DUB activity comparable to that of the DUBm with ATXN7-24Q. However, in vivo ATXN7-poly(Q) tends to form aggregates that sequester DUBm components away from their substrates. Incorporation into DUBm can help solubilize ATXN7-poly(Q) in vitro and in vivo, partially alleviating the formation of the poly(Q)-containing aggregates in astrocytes. Impaired DUB activity in the cerebellums of SCA7 patients expressing ATXN7-poly(Q) likely leads to increased global H2Bub levels, as well as the deregulation of other DUBm substrates, contributing to SCA7 disease.