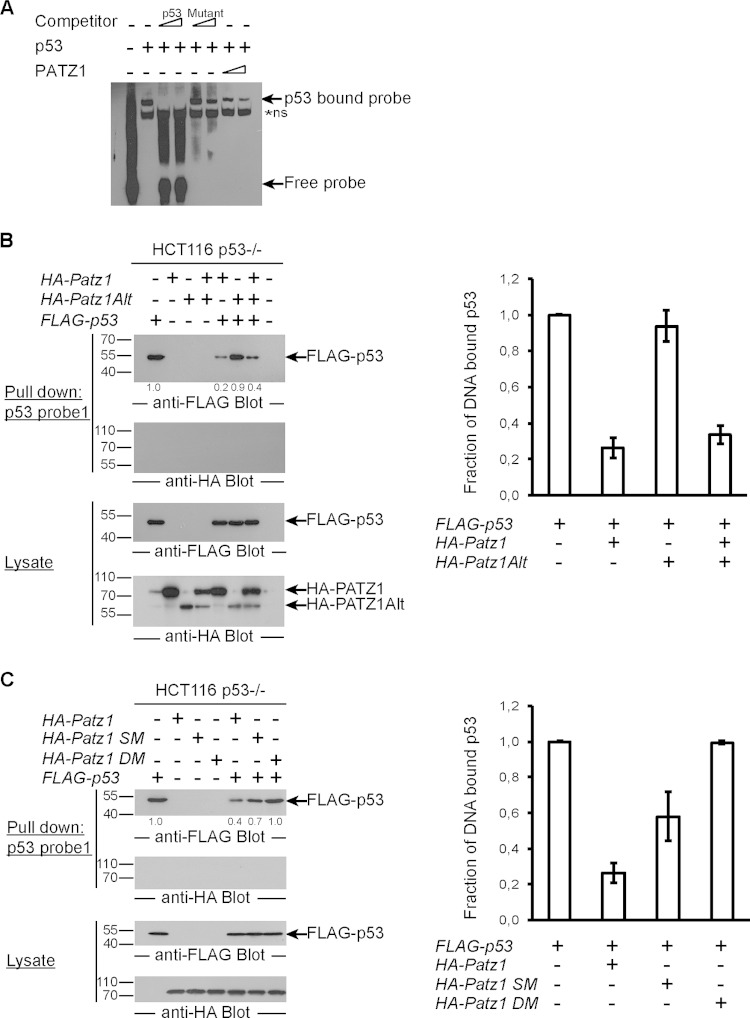
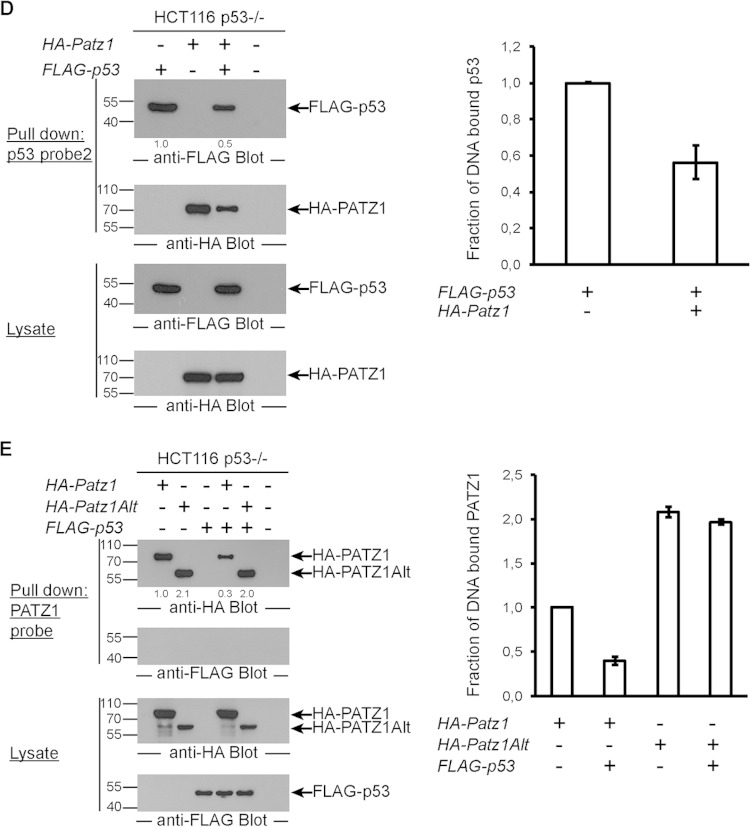
FIG 6.
PATZ1 inhibits p53 DNA binding. (A) p53 DNA binding in EMSAs is inhibited by PATZ1. Incubation of bacterially expressed His-tagged p53 with biotinylated p53 probes reveals a specific shifted band (lane 2). The specificity of this band was demonstrated by competition using an unlabeled p53 probe (lanes 3 and 4) and an unlabeled mutant p53 probe (lanes 5 and 6). Decreased levels of p53-dependent shifted bands are evident in the presence of PATZ1 (lanes 7 and 8). Triangles represent 2-fold increasing amounts of PATZ1 and competitor probes. *ns indicates a nonspecific band that cannot be competed away with competitor probes. (B) The PATZ1-p53 interaction inhibits p53 DNA binding to probe 1, derived from the pG13 p53 reporter. (Top and second panels) Precipitation followed by anti-FLAG (top) or anti-HA (second panel) antibody blotting reveals the presence of DNA-bound FLAG-p53 but not HA-PATZ1 (top, lane 1). FLAG-p53 continues to bind to DNA in the presence of HA-PATZ1Alt (top, lane 5) but not HA-PATZ1 (lane 4). (Third and bottom panels) Lysates of transfected cells show that FLAG-p53 (third panel) and HA-PATZ1 and HA-PATZ1Alt (bottom) are expressed at equal levels in transfected cells. The intensities of the relevant bands were quantified and normalized to the intensity of the lane with FLAG-p53 alone (indicated as values below the top panel). (C) PATZ1 mutants that do not bind p53 cannot inhibit p53 DNA binding. (Top and second panels) Precipitation followed by anti-FLAG (top) or anti-HA (second panel) antibody blotting reveals the presence of DNA-bound FLAG-p53 (lane 1). FLAG-p53 continues to bind to DNA in the presence of HA-PATZ1 DM (lane 7). Less FLAG-p53 is bound to DNA in the presence of HA-PATZ1 SM (lane 6), and dramatically reduced binding is seen in the presence of HA-PATZ1 (lane 5). (Third and bottom panels) Lysates of transfected cells show that FLAG-p53 (third panel) and HA-PATZ1 and the single and double mutants HA-PATZ1 SM and DM, respectively (bottom), are expressed at equal levels in transfected cells. The intensities of the relevant bands were quantified and normalized to the intensity of the lane with FLAG-p53 alone (indicated as values below the top panel). (D) The PATZ1-p53 interaction inhibits p53 DNA binding to alternative probes (probe 2; derived from the Gadd45 promoter). (Top and second panels) Precipitation followed by anti-FLAG (top) or anti-HA (second panel) antibody blotting reveals the presence of DNA-bound FLAG-p53 (top, lane 1), and surprisingly, HA-PATZ1 (second panel, lane 2). FLAG-p53 (top, compare lanes 1 and 3) and HA-PATZ1 (second panel, compare lanes 2 and 3) cannot bind to this DNA probe as efficiently in the presence of the other protein. (Third and bottom panels) Lysates of transfected cells show that FLAG-p53 (third panel) and HA-PATZ1 (bottom) are expressed at equal levels in transfected cells. The intensities of the relevant bands were quantified and normalized to the intensity of the lane with FLAG-p53 alone (indicated as values below the top panel). (E) The PATZ1-p53 interaction inhibits PATZ1 DNA binding to PATZ1 probes. (Top and second panels) Precipitation followed by anti-HA (top) or anti-FLAG (second panel) antibody blotting reveals the presence of DNA-bound HA-PATZ1 or HA-PATZ1Alt (top, lanes 1 and 2) but not FLAG-p53 (second panel, lane 3). HA-PATZ1 cannot bind to its probe in the presence of FLAG-p53 as efficiently (top, lane 4). However, the presence of FLAG-p53 does not affect DNA binding of PATZ1Alt (top, lane 5). (Third and bottom panels) Lysates of transfected cells show that FLAG-p53 (bottom) and HA-PATZ1 and HA-PATZ1Alt (third panel) are expressed at equal levels in transfected cells. The intensities of the relevant bands were quantified and normalized to the intensity of the lane with HA-PATZ1 alone (indicated as values below the top panel). (B to E) Biotinylated DNA probes incubated with lysates from HCT116 p53−/− cells transfected with the indicated plasmids were precipitated with streptavidin-conjugated magnetic beads. Pulldown experiments were repeated at least 3 times with independent lysates, and averages of data for the quantitation of the bands observed in Western blots are depicted as bar graphs on the right. Error bars indicate standard errors of the means.