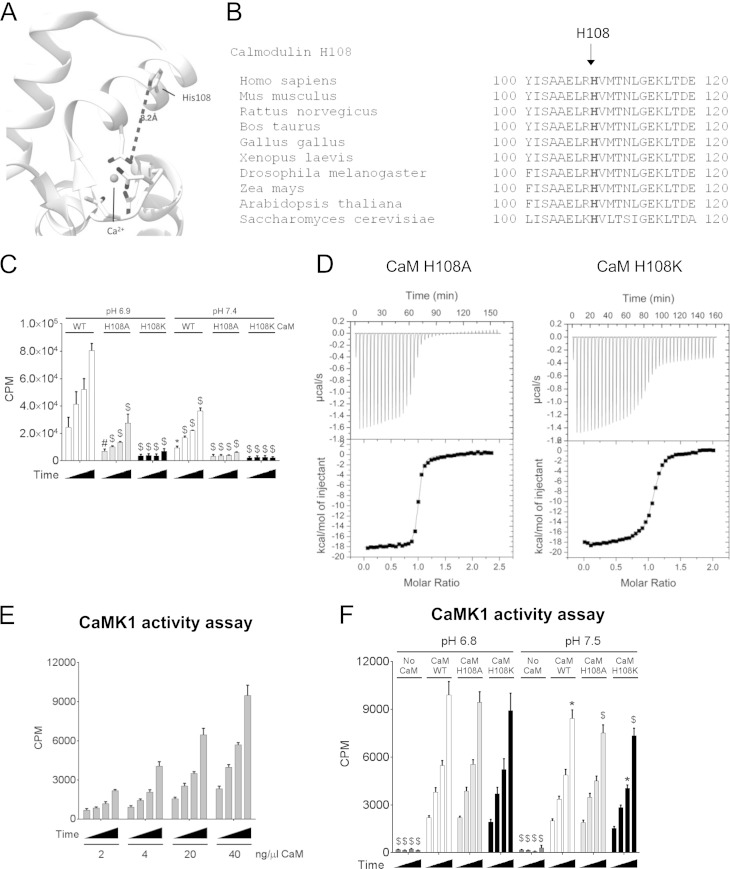
FIG 8.
CaM H108 is essential for eEF2K activation. (A) Ribbon diagram of the closed CaM structure (PDB code 1CDL). The histidine (H108) and residues coordinating the Ca2+ ions are shown as sticks, and the Ca2+ ion is shown as a sphere. (B) Sequence alignment of CaM(110–120) among species. (C) eEF2K kinase assay using wild-type CaM or the H108A or H108K mutant of CaM at pH 6.9 and pH 7.4. (D) Calorimetric titrations of CaM mutants with eEF2K(78–100) at pH 6.8. eEF2K(78–100) peptide corresponds to the sequence of the CaM-binding site in eEF2K(78–100). P values were obtained by two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test (control, pH 6.9, wild-type eEF2K). (E) CaMK1 activity assay at pH 6.8 with the indicated amount of CaM per assay. (F) CaMK1 activity assay using 16 μg of wild-type CaM of the H108A or H108K mutant of CaM at pH 6.9 and pH 7.4. Results are expressed as means ± SE from 3 (in panels C and E) or 4 (in panel F) independent experiments. *, 0.01 ≤ P < 0.05; #, 0.01 < P ≤ 0.001; $, P < 0.001. For data in panel F, P values were obtained by two-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test (control, pH 6.9, wild-type eEF2K and wild-type CaM).