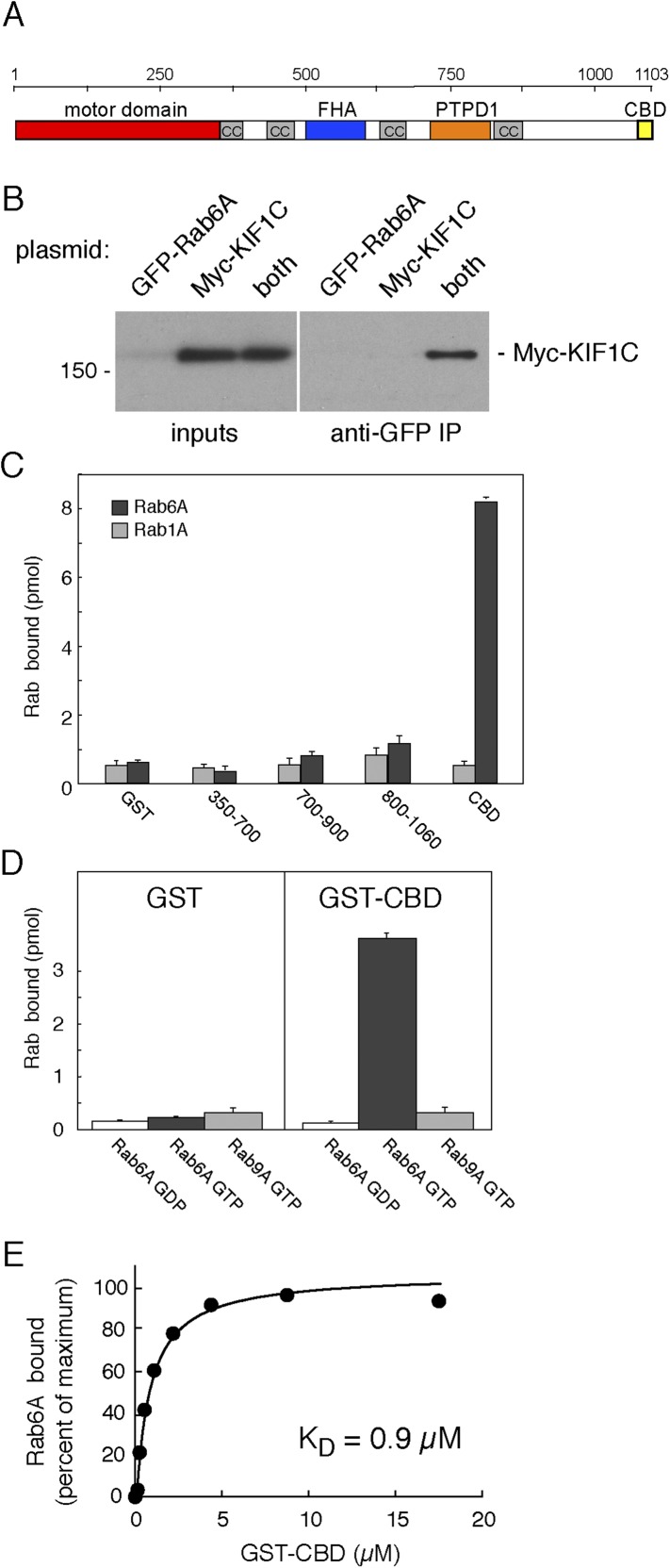
Figure 1. KIF1C binds Rab6A GTPase.
(A) KIF1C schematic showing the N-terminal motor (red), predicted coiled-coil (cc, gray), Forkhead homology (FHA, blue), protein tyrosine phosphatase D1 binding (PTPD1, orange), and C-terminal Rab binding (CBD, yellow) domains (AA 1060-1103). (B) KIF1C co-immunoprecipitation by Rab6A. HEK293 cells were transfected with GFP-Rab6A, myc-KIF1C, or both. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with llama GFP-binding protein and immunoblotted with anti-myc antibody. Left panel, total soluble cell lysates, 5%; right panel, bound fraction, 33%. (C) Domain specificity of Rab6A binding. His-Rab6A-35S-GTPγS (black bars) or His-Rab1A-35S-GTPγS (gray bars) (1 μM) binding to GST-KIF1C constructs (15 μM) pulled-down with glutathione Sepharose and quantified by liquid scintillation counting (error bars = SD). (D) Nucleotide specificity of Rab6A binding. Binding of His-Rab6A or His-Rab9A (500 nM) preloaded with 35S-GTPγS or 3H-GDP to GST or GST-KIF1C CBD (15 μM) was assayed as in C (error bars = SD). (E) His-Rab6A Q72L binds to GST-KIF1C CBD in a concentration-dependent manner. GTPγS-loaded His-Rab6A Q72L (0.58 μM) binding to GST-KIF1C CBD (immobilized on glutathione Sepharose) as determined by quantitative fluorescent antibody immunoblot, presented as a fraction of maximal binding (2.2% of total). Data were fit using GraphPad Prism software.