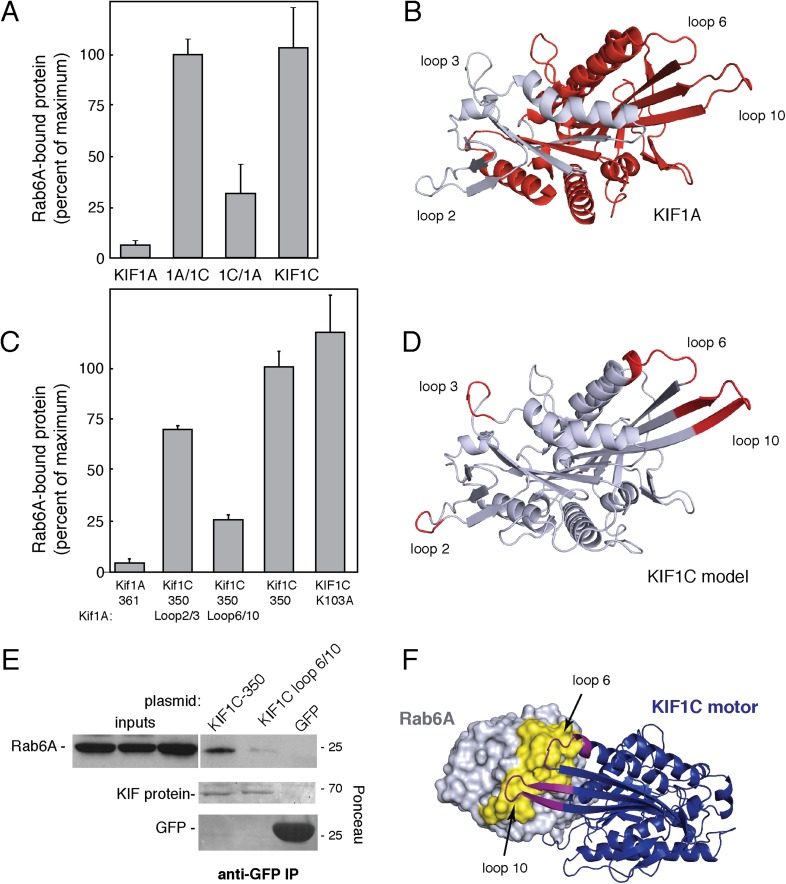
Figure 4. KIF1C loops 6 and 10 are necessary for Rab6A binding.
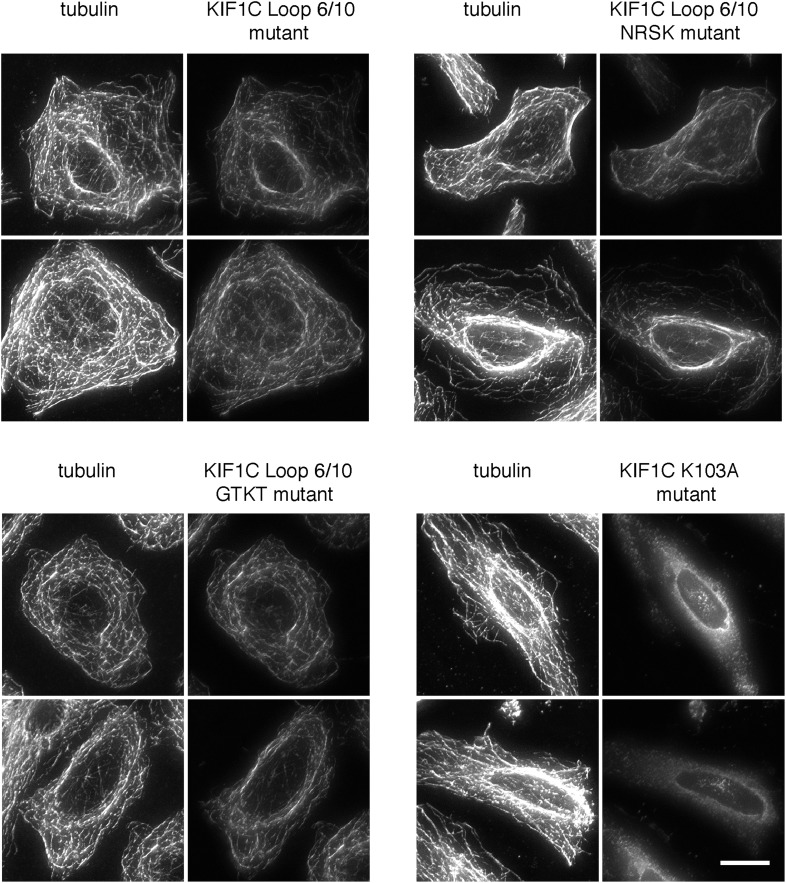
(A) Binding of in vitro translated myc-KIF1A (1–361), myc-KIF1A/1C, myc-KIF1C/1A, and myc-KIF1C-350 motor domain chimera constructs to GTPγS-loaded GST-Rab6A Q72L (0.2 μM) presented as a percentage of maximal KIF1C bound (24.7% of input). (B) Crystal structure of KIF1A showing the regions swapped between KIF1A and KIF1C. The C-terminal portion is colored red. (C) Binding of in vitro translated myc-KIF1A (1–361), myc-KIF1C-350 Loop 2/3 swap, myc-KIF1C-350 Loop 6/10 swap, myc-KIF1C-350, and myc-KIF1C-350 K103A constructs to GTPγS-loaded GST-Rab6A Q72L (0.2 μM) presented as a percent of myc-KIF1C-350 bound (35.3% of input). (D) Predicted crystal structure of KIF1C with Loop 2/3 (at left), 6/10 (at right) labeled in red. The KIF1C sequence was overlaid onto the KIF1A crystal structure (PDB 2ZFI) using PHYRE2. (E) Binding of endogenous Rab6A to transiently expressed CFP-KIF1C-350, CFP-KIF1C-350 Loop 6/10 swap, and GFP immunoprecipitated with llama GFP-binding protein, as determined by anti-Rab6A immunoblot. Total endogenous Rab6A (2%) at left compared to bound (33%) at right. Below, bound CFP-KIF1C and GFP as measured by Ponceau S staining. (F) Molecular docking of Rab6A onto the predicted structure of KIF1C. The predicted structure (blue) was docked to the crystal structure of Rab6A (PDB 2Y8E, gray) using ClusPro2. The model for the largest cluster containing 144 members is shown. The switch regions of Rab6 are labeled in yellow and loop 6 and 10 of KIF1C are labeled in purple. Error bars represent SD.