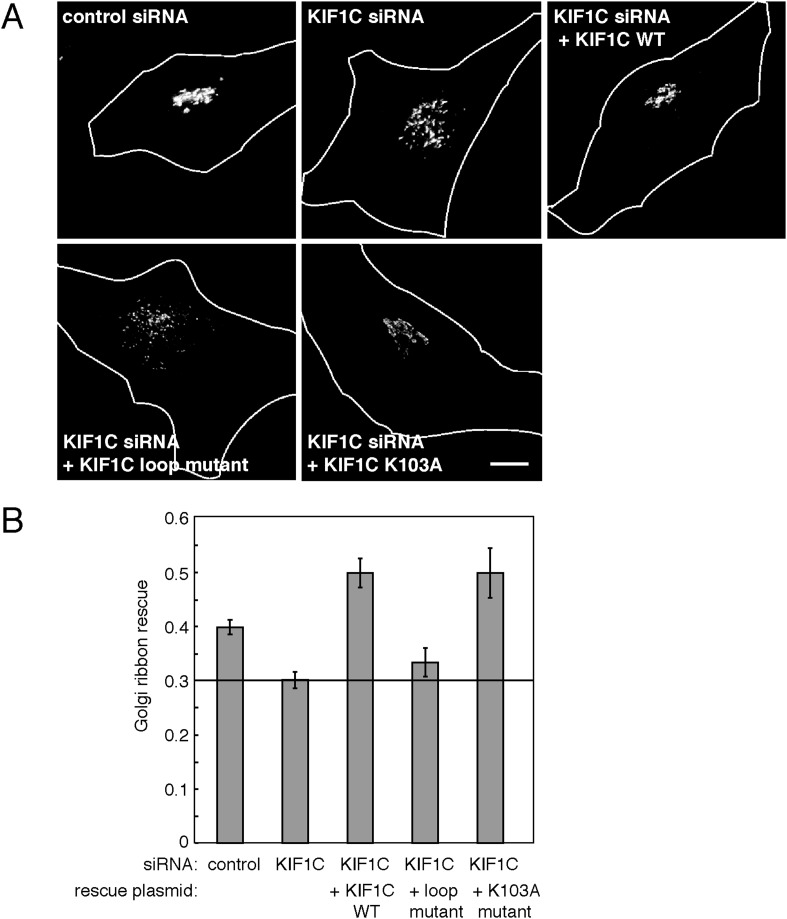
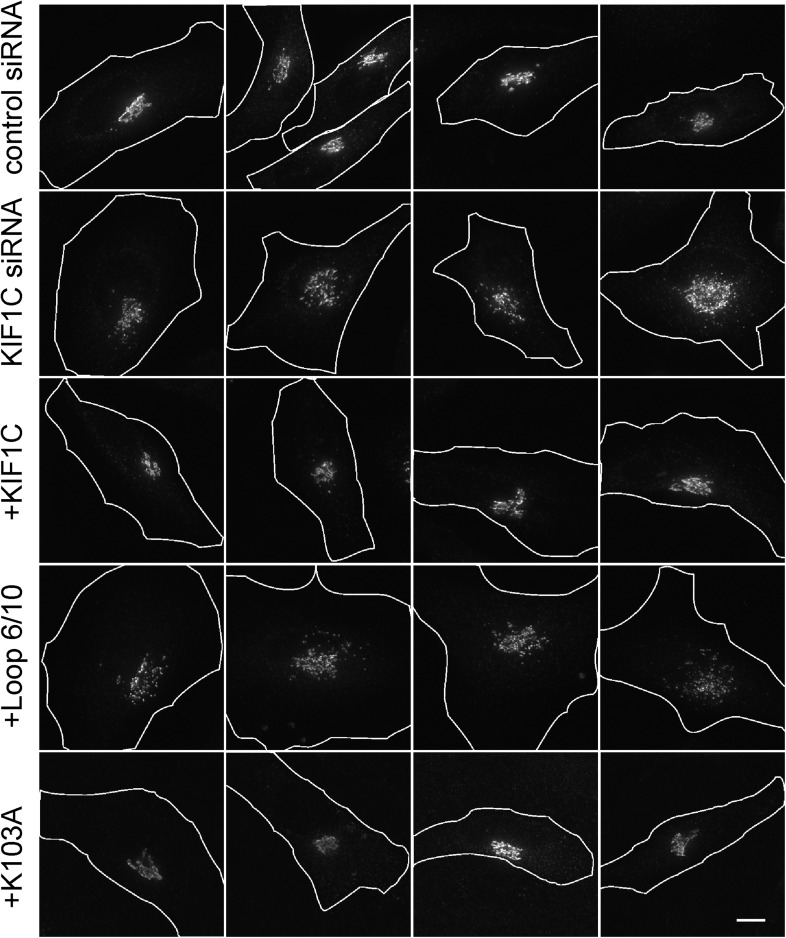
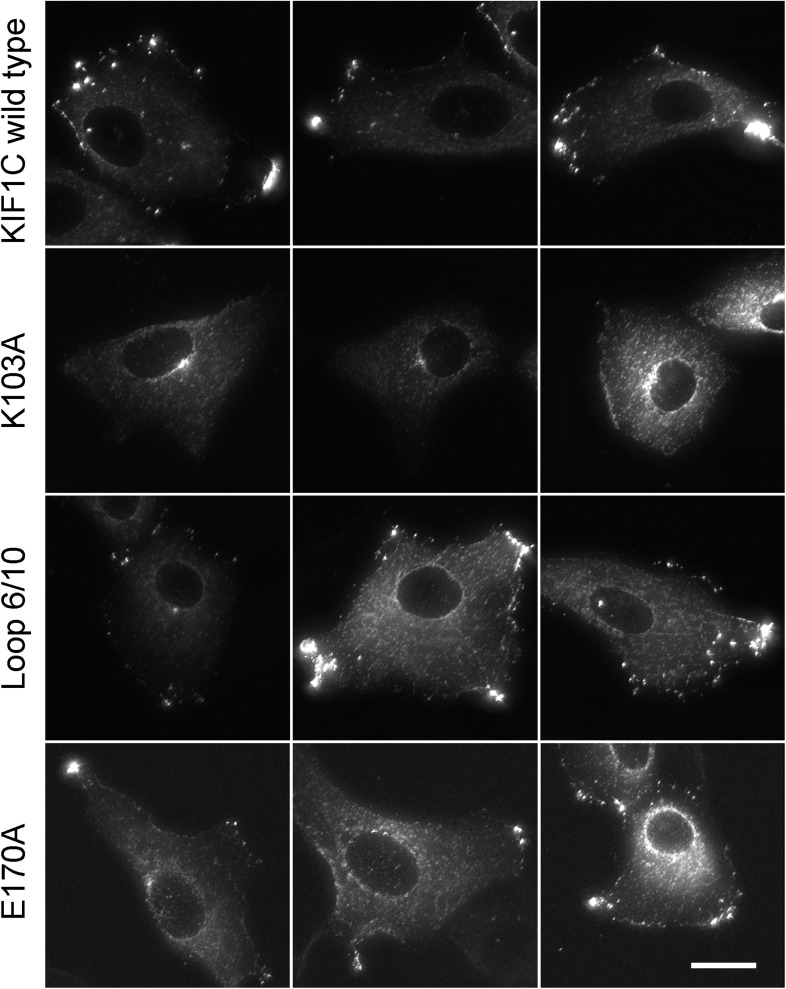
Figure 8. KIF1C's N-terminal Rab6A binding site is required for the maintenance of Golgi morphology.
(A) Golgi morphology (p115) of HeLa cells transfected with control siRNA or KIF1C siRNA and the indicated rescue plasmid. Scale bar, 10 µm. (B) Golgi ribbon rescue, defined as the mean fraction of Golgi staining present as large objects (>4.11 µm²), normalized by KIF1C intensity, quantified from cells such as those shown in A (bars = SE, >90 cells/condition). KIF1C wild-type rescue cells were statistically different from KIF1C depleted and loop mutant rescue cells but not those rescued with KIF1C K103A (p < 0.001).