Figure 4.
Mapping the TARP γ-2 Contact Region on GluA2
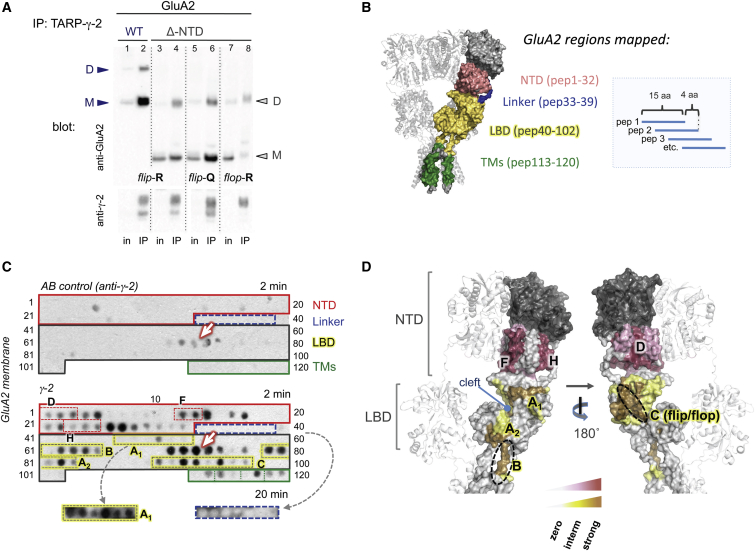
(A) coIP of GluA2 variants with TARP γ-2. The blot was probed with polyclonal GluA2 antibody (top panel) and anti γ-2 (bottom panel). Both WT and ΔNTD protein migrated as monomer (M) and dimer (D), denoted by arrowheads. Note that while inputs were comparable, amounts of IPed GluA2 varied between conditions.
(B) Schematic of the peptide array layout (right). Each peptide is spotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane (C). Peptide coverage of the rat GluA2 sequence is outlined in the left panel in color code as indicated. The four GluA2 regions—the NTD lower lobe, the NTD-LBD linkers, the LBD, and the TM segments of the channel—are highlighted. GluA2 peptide numbers covering each domain are indicated in brackets.
See Table S1 for peptide sequences.
(C) Regions of GluA2 binding to TARP γ-2. (Upper panel) Nonspecific signal, resulting from anti-γ-2 antibody binding to GluA2 in the absence of the γ-2 probe (“AB control”). AMPAR domains are highlighted in boxes and match the color scheme in (B). Peptide numbers are indicated on the side. The membrane was exposed to an X-ray film for 2 min; the arrow denotes nonspecific signals. (Lower panel) The same membrane was probed with full-length TARP γ-2 and detected with anti-γ-2 AB followed by a HRP-labeled secondary AB (2 min exposure). Individual AMPAR secondary structure elements, corresponding to NTD and LBD helices, are highlighted in stippled boxes on the blot (compared with D). The bottom panel shows a longer exposure for the LBD-A1 region (yellow) and the NTD-LBD linker (blue).
See Figure S4A for a longer exposure of the blot.
(D) TARP binding sites deduced from the peptide array in (C) are mapped onto the extracellular region of GluA2 (PDB: 3KG2). NTD interaction sites are denoted in deep red (strong interaction) and light pink (weaker interaction; see graded bar below), with alpha helices contacted by γ-2 denoted by (D), (F), and (H). LBD interaction sites are highlighted in brown (strong interaction) and yellow (weaker interaction). The three core contact regions, A–C, are denoted. Region A spans the glutamate binding cleft (interaction sites A1 and A2); region B encompasses the LBD-TM linker 1, and region C corresponds to the flip-flop cassette (denoted with a stippled ellipsoid).
See also Figures S3, S4, and S6 and Table S1.