Figure 4.
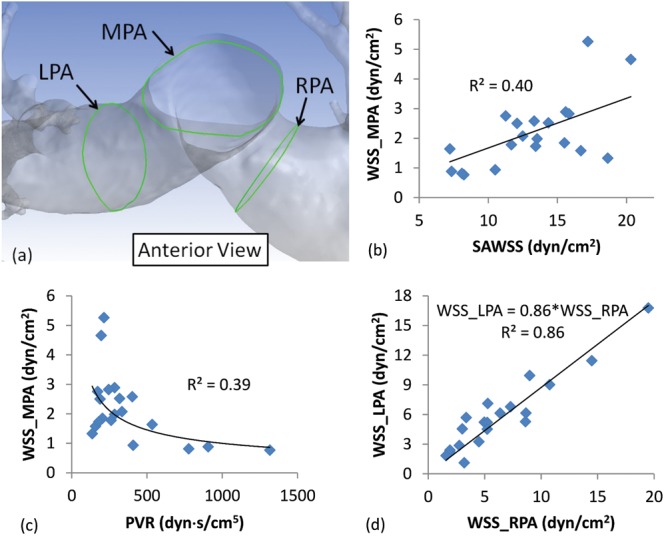
a, Schematic showing a sample reconstructed pulmonary vasculature, with lines along the endothelium found at the intersection of the main, right, and left pulmonary arteries (MPA, RPA, and LPA, respectively) and three arbitrary planes normal to the centerline of the lumen at these vessels, represented by the green lines. Average wall shear stress (WSS) was measured along these lines (WSS_MPA, WSS_RPA, and WSS_LPA), which is the typical WSS that can be calculated from phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging (PC-MRI). b, A weak correlation between WSS_MPA (typically available from PC-MRI) and spatially averaged WSS (SAWSS, available from computational fluid dynamics simulations). This weak relationship could suggest that the inconsistency (between patients) in locating the plane of interest for PC-MRI could make the imaging technique unsatisfactory for approximating patient-specific pulmonary endothelium WSS distribution. c, A weak correlation between WSS_MPA and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) suggests that approximating WSS from PC-MRI might not be accurate for predicting right ventricular afterload. d, A strong correlation between WSS_LPA and WSS_RPA values suggests a consistent flow distribution in the vasculature and a relatively similar velocity profile downstream of the bifurcation. Note that all correlations satisfied the criterion for statistical significance, P < 0.05.
