Table 3.
Cardiorespiratory variables during voluntary hyperpnoea at different percentages of maximal exercise ventilation
45% 
|
60% 
|
75% 
|
100% 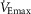
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Men | Women | Men | Women | Men | Women | Men | Women |
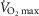 (% max) (% max) |
70 ± 3 | 72 ± 3 | 83 ± 1 | 83 ± 2 | 92 ± 1 | 92 ± 2 | 100 | 100 |
| VT (l) | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 1.7 ± 0.1* | 3.3 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.1* | 3.3 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.1* | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 1.8 ± 0.1* |
| fR (breaths min−1) | 27 ± 2 | 34 ± 2* | 33 ± 2 | 39 ± 2 | 41 ± 3 | 46 ± 2 | 53 ± 2 | 60 ± 2* |
| ΔHR (beats min−1) | 0 ± 3 | −2 ± 3 | 7 ± 2 | 6 ± 4 | 7 ± 1 | 11 ± 3 | 20 ± 3 | 25 ± 3 |
| tE/ttot | 0.55 ± 0.01 | 0.55 ± 0.01 | 0.54 ± 0.01 | 0.55 ± 0.01 | 0.53 ± 0.01 | 0.55 ± 0.01 | 0.51 ± 0.01 | 0.53 ± 0.01 |
 (mmHg) (mmHg) |
40 ± 1 | 37 ± 1 | 40 ± 1 | 37 ± 1 | 35 ± 1 | 36 ± 1 | 31 ± 2 | 35 ± 2 |
 (l min−1) (l min−1) |
81 ± 7 | 55 ± 2* | 106 ± 5 | 71 ± 3* | 133 ± 7 | 88 ± 3* | 165 ± 4 | 109 ± 4* |
 / /  (ml O2 l−1) (ml O2 l−1) |
1.4 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 2.4 ± 0.2* | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 3.5 ± 0.3* |
 /WOB (ml O2 J−1) /WOB (ml O2 J−1) |
0.8 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.1* | 0.8 ± 0.05 | 1.2 ± 0.1* | 0.7 ± 0.04 | 1.1 ± 0.1* | 0.7 ± 0.0 | 1.1 ± 0.1* |
| EfficiencyRM (%) | 6.7 ± 0.5 | 5.1 ± 0.6* | 6.4 ± 0.4 | 4.4 ± 0.3* | 7.7 ± 0.94 | 4.8 ± 0.3* | 7.2 ± 0.2 | 4.6 ± 0.4* |
| ΔPoe (cmH2O) | 24 ± 1 | 19 ± 2 | 31 ± 2 | 24 ± 2 | 39 ± 3 | 32 ± 2 | 55 ± 4 | 47 ± 3* |
| WOB (J min−1) | 142 ± 21 | 75 ± 8 | 232 ± 23 | 122 ± 12* | 347 ± 38 | 199 ± 15* | 593 ± 60 | 339 ± 27* |
| WOBres (% total) | 40 ± 3 | 51 ± 5* | 57 ± 3 | 54 ± 5 | 65 ± 3 | 65 ± 4 | 76 ± 2 | 76 ± 3 |
| WOBel (% total) | 60 ± 3 | 49 ± 6* | 43 ± 3 | 46 ± 5 | 35 ± 3 | 35 ± 4 | 24 ± 2 | 24 ± 3 |
| EELV (% FVC) | 35 ± 2 | 44 ± 3* | 33 ± 1 | 44 ± 3* | 32 ± 1 | 43 ± 2* | 38 ± 2 | 46 ± 3* |
| EILV (% FVC) | 83 ± 2 | 83 ± 3 | 85 ± 2 | 86 ± 3 | 85 ± 2 | 88 ± 2 | 87 ± 1 | 88 ± 1 |
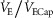 (%) (%) |
38 ± 3 | 33 ± 3 | 52 ± 3 | 40 ± 3* | 67 ± 3 | 51 ± 3* | 74 ± 4 | 67 ± 4 |
Abbreviations: EELV, end-expiratory lung volume; EfficiencyRM, efficiency of the respiratory muscles determined by dividing the measured  by the calculated ideal oxygen uptake needed to perform the work; EILV, end-inspiratory lung volume; fR, breathing frequency; ΔHR, change in heart rate from rest to mimic;
by the calculated ideal oxygen uptake needed to perform the work; EILV, end-inspiratory lung volume; fR, breathing frequency; ΔHR, change in heart rate from rest to mimic;  , end-tidal carbon dioxide tension; ΔPoe, oesophageal pressure swing; tE, expiratory time; ttot, total breath time;
, end-tidal carbon dioxide tension; ΔPoe, oesophageal pressure swing; tE, expiratory time; ttot, total breath time;  , minute ventilation;
, minute ventilation;  , ventilatory capacity;
, ventilatory capacity;  , maximal oxygen uptake; VT, tidal volume;
, maximal oxygen uptake; VT, tidal volume;  , respiratory muscle oxygen uptake; WOB, work of breathing; WOBel, elastic work of breathing; and WOBres, resistive work of breathing. *Significantly different from men (P < 0.05).
, respiratory muscle oxygen uptake; WOB, work of breathing; WOBel, elastic work of breathing; and WOBres, resistive work of breathing. *Significantly different from men (P < 0.05).
