Figure 4. Effect of clenburerol on SOL myofibrilar ATPase activity in relaxed (A–E) and Ca2+-activated (F–H) conditions at 4°C.
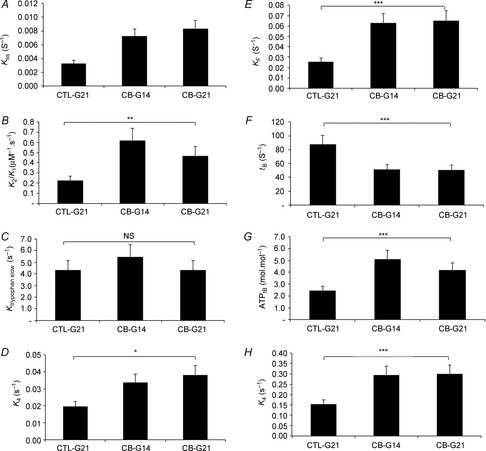
Reaction mixture concentrations were 3 and 30 μm for myosin heads and [γ-32P]ATP concentrations in Rapid Flow Quench experiments, respectively. In Stopped-Flow experiments (B and C), myosin head concentration was 1 μm reaction mixture, and ATP concentrations ranged from 30 μm to 1 mm. CTL-G21, control group; CB-G14, 14-day clenburerol-treated group; CB-G21, 21-day clenburerol-treated group; kSS, rate constant of the steady-state phase in relaxed condition; k2/K1, ATP binding-induced myosin detachment obtained from the initial slope of the regression of ktrypophan fast as a function ATP concentration; ktryprophan slow, rate constant observed for the slow phase of tryptophan increase when mixing myofibrils with ATP; k4, rate constant of Pi release (the isomerization step preceding diffusion of Pi); kF, rate constant of the fast steady-state phase in activated condition; tB, duration of the unloaded shortening phase, an index of unloaded shortening velocity; ATPtB, ATP consumed during the unloaded shortening phase. Because no significant difference was detected between CTL-G9, CTL-G14 and CTL-G21 groups, results of the CTL-G21 group are presented. NS, not significant. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
