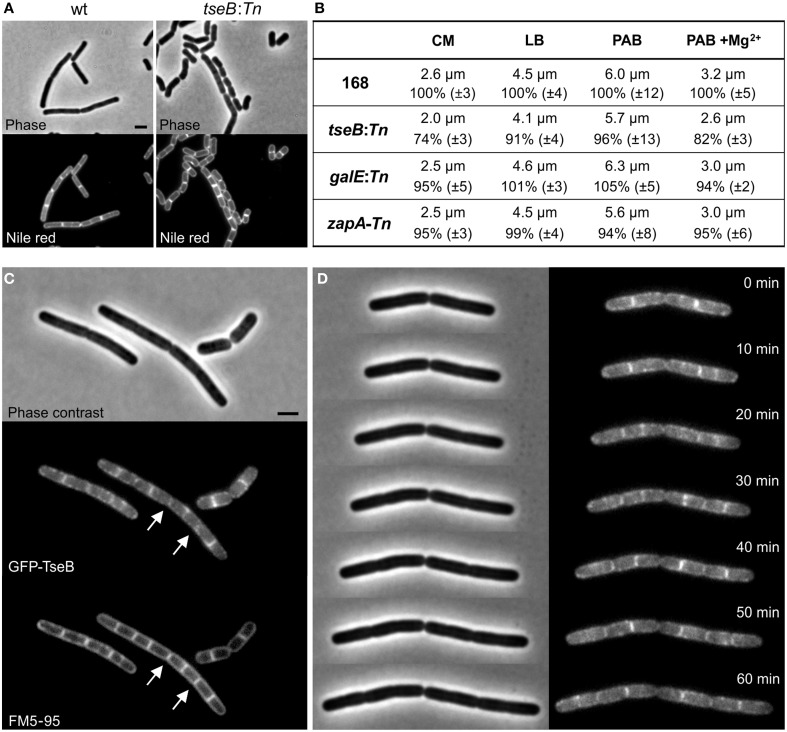
Figure 7.
Phenotype of ΔtseB and localization of GFP-TseB. (A) Phase contrast and membrane stain (Nile red) images of wild type strain 168 and the tseB mutant strain PG135 (tseB:TnYLB-1) grown in competence medium at 37°C. Scale bar 2 μm. (B) Cell length measurements of the transposon mutants in different growth media. Strains 168, tseB:TnYLB-1(PG135), galE:TnYLB-1 (PG143) and zapA-TnYLB1-yshB (PG140), were grown at 37°C in competence medium (CM), LB, PAB, or PAB supplemented with 5 mM Mg2+. Averaged absolute and relative cell lengths are presented below in %, and standard deviations are shown in brackets. One hundred to one hundred and fifty cells were measured in each experiment in triplicate. (C) Localization of GFP-TseB. Strain PG718 (amyE::Pxyl-mgfp-tseB) was grown in competence medium at 30°C with 0.5% xylose to express GFP-TseB. GFP, membrane stain (FM5-95) and phase contrast images were taken during exponential growth. Scale bar 2 μm. Arrows highlight some of the septa in which the GFP signal is absent. (D) Time-lapse microscopy experiment showing dynamic localization of GFP-TseB. Strain PG718 (amyE::Pxyl-mgfp-tseB) was grown at 30°C on a microscope slide made of competence medium supplemented with 0.5% xylose. GFP and phase contrast images were taken every 10 min.