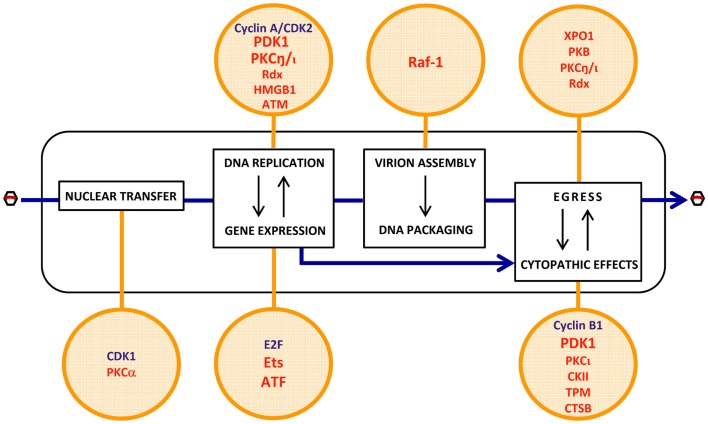
Figure 3.
Putative cell determinants of PV oncoselectivity. Indicated steps of the PV life-cycle (rectangles) were shown to be controlled by cellular factors (circles) known to be regulated at gene amplification, expression, and functional levels by cell proliferation (blue) and oncogenic transformation (red). The list of factors is not exhaustive and exemplifies candidate mediators of the enhanced permissiveness of neoplastic cells for PV infection. Evidence of the contribution of these factors to PV oncotropism is experimental for a few of them (PDK1, PKCη, Ets, ATF, Raf-1) but circumstantial for the others. For more details, see main text (pp. 4–5). CDK2, cyclin-dependent kinase 2; PDK1, phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1; PKC, protein kinase C; Rdx, radixin; HMGB1, high-mobility group box protein 1; ATM, ataxia-telangiectasia mutated protein; Raf-1, rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma-1 protein; XPO1, exportin-1; PKB, protein kinase B; E2F, transcription factor E2F; Ets, E26 transformation-specific transcription factor; ATF, activating transcription factor; CKII, casein kinase II; TPM, tropomyosin; CTSB, cathepsin B.