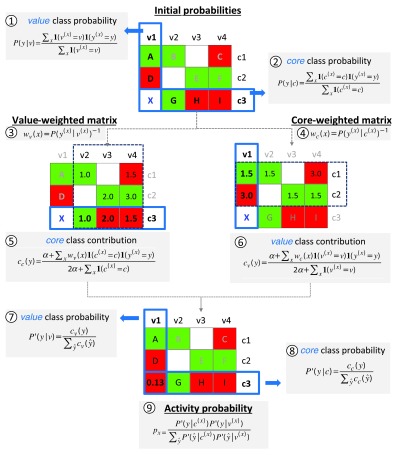
Figure 3. Predictions based on conditional probabilities of activity.
Steps and equations required to derive probabilities of activity from SARMs for prediction of virtual compound X are shown using a model SARM with nine compounds (A–I) that contain three cores ( c1– c3) and four values ( v1– v4). Matrix cells are color-coded according to compound activity (red, inactive; green, active). In the first step, initial class probabilities are calculated for all cores and values using equation 2 and 1, respectively. Value- and core-weighted matrices are then derived via equations 4 and 3. The class contribution of core c3 is obtained from the value-weighted matrix using equation 5. Analogously, the class contribution of value v1 is obtained from the core-weighted matrix using equation 6. The value and core class contributions are then normalized using equations 7 and 8. Finally, the activity probability p x of 0.13 is obtained for X by combining the normalized core c3 and value v1 class probabilities using equation 9.