Figure 1.
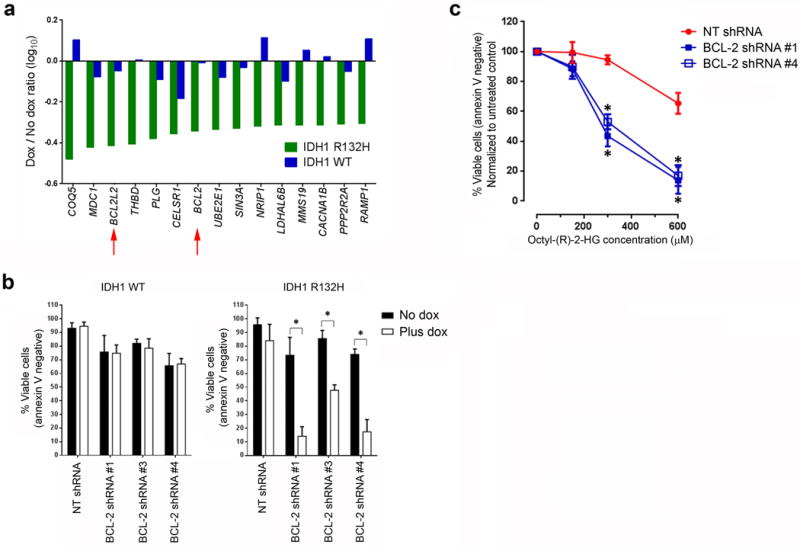
Identification of BCL-2 as synthetic lethal to mutant IDH1. (a) The 15 synthetic lethal gene hits. The log10 of the drop-out ratio (number of barcode reads in the presence of dox to the number of reads in the absence of dox) in mutant IDH1R132H-expressing cells (green bars) or in wild-type IDH1-expressing cells (blue bars) is shown. The red arrows highlight two antiapoptotic members of the BCL-2 family. (b) Viability of the engineered THP-1 cell lines transduced with lentiviral vectors encoding the indicated shRNAs and induced to express either wild-type or mutant IDH1R132H for seven days. The means of three biological replicates are shown. (c) Viability of parental THP-1 cells transduced with lentiviral vectors encoding the indicated shRNAs and treated with the indicated concentrations of octyl-(R)-2-HG for two days. The means of three biological replicates are shown. NT, non-targeting. *P < 0.05. Statistical significance (P) was determined by Student’s t-test. All error bars represent sd.
