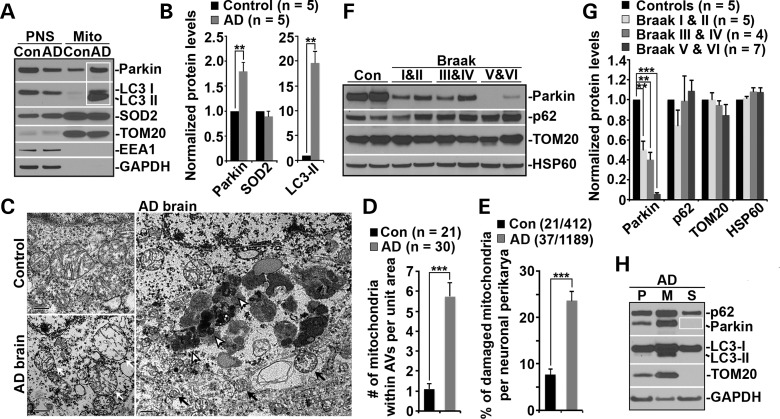
Figure 5.
Parkin-mediated mitophagy in AD patient brains. (A and B) Increased levels of Parkin and LC3-II associated with purified mitochondria from AD patient brains. Following Percoll-gradient membrane fractionation, equal amount (5 μg) of mitochondria-enriched membrane fractions (Mito) and post-nuclear supernatant (PNS) fractions from brains of control and AD patients were sequentially immunoblotted with antibodies against Parkin and various markers including LC3 (autophagy), TOM20 and SOD2 (mitochondria), EEA1 (early endosome) and GAPDH (cytosol). Data were quantified from five independent repeats. (C–E) Representative TEM micrographs showing a striking accumulation of autophagic vacuoles (AVs) engulfing abnormal mitochondria in the hippocampus of AD patients (C). Clustered AV-like organelles and abnormal mitochondria with swollen shape and loss of cristae integrity were consistently observed in neuronal perikarya of AD patient brains. Quantitative analysis was expressed as the average number of mitochondria within AV-like organelles (D) and percentage of morphologically abnormal mitochondria (E) per neuronal perikarya in the cross section (10 μm × 10 μm). While black open arrows point to AVd-like organelles, black solid arrows mark AVi-like structures engulfing or containing damaged mitochondria. White arrows denote swollen mitochondria with perturbed or loss of inner structure in AD brain. Data were quantified from a total number of cells (n) (D) or a total number of cells and mitochondria (E) as indicated in parentheses from four different AD brains and two control brains. Scale bars: 500 nm. (F and G) Representative blots (F) and quantitative analysis (G) showing progressive Parkin reduction in AD patient brains. Twenty micrograms of brain homogenates from the cortices of age-matched controls and AD patients were sequentially detected on the same membrane. Relative protein levels were normalized to those of control subjects. Note that reduced Parkin levels were consistently observed in AD patient brains. Data were analyzed from the number of human brain samples as indicated in parentheses. (H) Representative blots showing depletion of cytosolic Parkin in AD patient brains. AD cortical tissues were subjected to fractionation into post-nuclear supernatant (P), mitochondrial-enriched membrane fraction (M) and cytosolic supernatant (S). An equal amount of protein (5 μg) of the three fractions was sequentially immunoblotted with antibodies against autophagy markers p62/SQSTM1, Parkin and LC3, mitochondrial marker TOM20 and cytosolic protein GAPDH on the same membranes after stripping between each antibody application. Error bars: SEM. Student's t-test: ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05. APP, amyloid precursor protein; Aβ, amyloid-β; AD, Alzheimer's disease; WT, wild-type; Tg, transgenic; DIV, days in vitro; TMRE, tetramethylrhodamine ethyl ester; CCCP, carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazone; Cyto c, cytochrome c; Δψm, mitochondrial membrane potential; AV, autophagic vacuole; LAMP-1, lysosome-associated membrane protein-1; LC3, microtubule-associated protein light chain 3; Mito, mitochondria.