Fig 1. Genetic dissection of codY mutants.
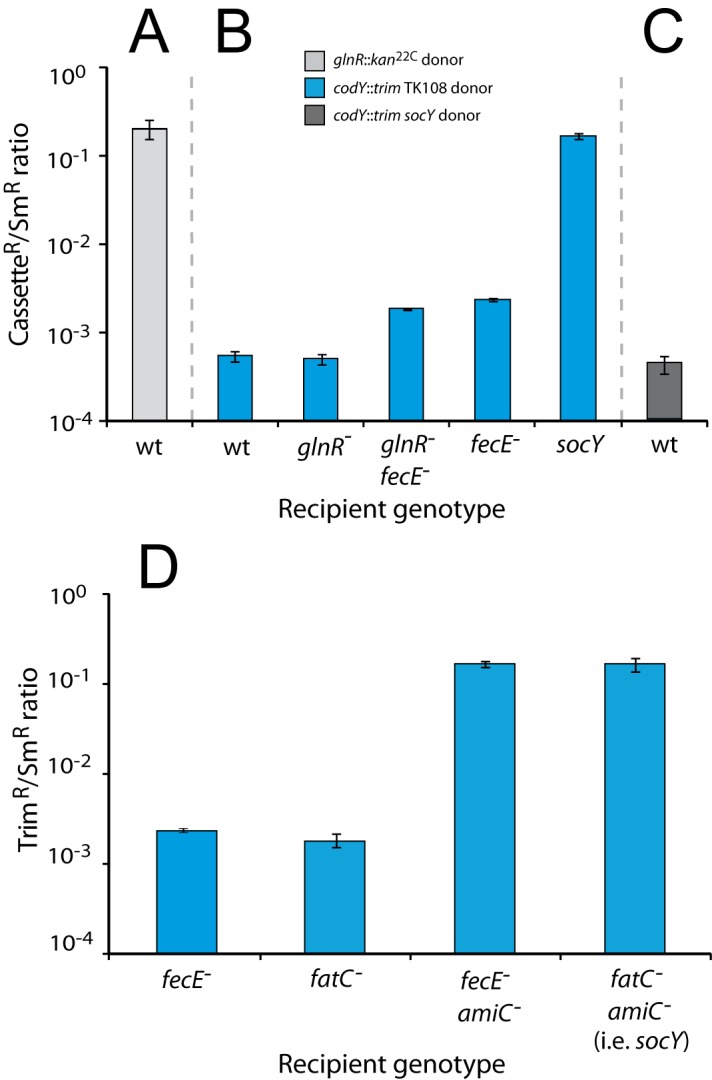
(A) Transformation efficiency of the glnR::kan 22C cassette into wildtype (wt) recipient. Transformation efficiencies calculated from triplicate repeats. Donor strain, R3154; wt recipient strain, TD198. (B) Transformation efficiency of the codY::trim cassette present in the glnR codY (fecE) mutant into wt and mutant recipient strains. Transformation efficiencies calculated as in panel A. Donor strain, TD196 (i.e. TK108 but rpsL41). Recipient strains, wt, TD198; glnR -, TD195; glnR - fecE -, TD227; fecE -, TD230; socY, TD142. (C) Transformation efficiency of the codY::trim cassette from the suppressed codY::trim, socY strain into a wt recipient. Transformation efficiencies calculated as in panel A. Donor strain, TD80; wt recipient as in panel A. (D) Inactivation of fatC and fecE has the same suppressive effect on codY inactivation. Transformation efficiency of the codY::trim cassette present in the TK108 mutant into wt and mutant recipient strains. Transformation efficiencies calculated as in panel A. Donor strain, TD196. Recipient strains, fecE -, TD230; fatC -, TD141; fecE - amiC -, TD228; socY, TD142.
