Fig 1.
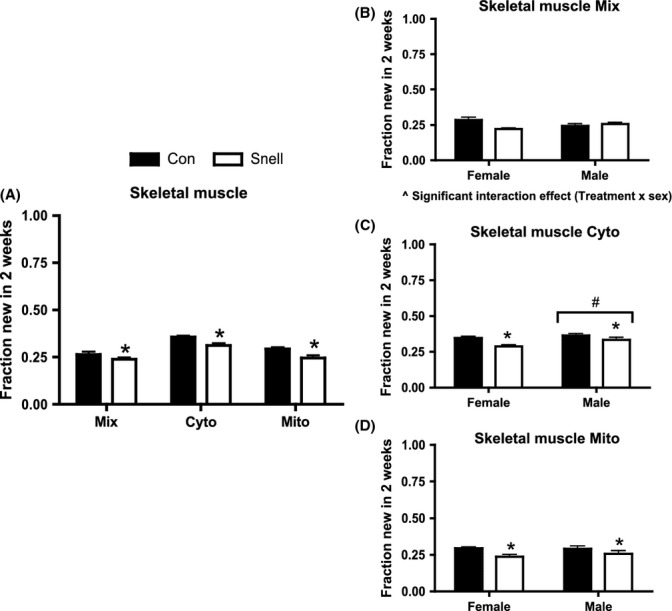
Protein synthesis in skeletal muscle and between sexes over 2 weeks in Snell and Con. Protein synthesis was significantly decreased in Snell compared to Con in Mix, Cyto, and Mito fractions (A). In Mix, there was a significant interaction between treatment (Snell) and sex (B). Protein synthesis was decreased in both female and male Snell compared to their respective Con in Cyto and Mito (C, D). Independent of treatment, Cyto protein synthesis was increased in males compared to females (C). n = 5 per sex and n = 10 per group. *P < 0.05 for Snell vs. Con; #P < 0.05 difference between sexes independent of treatment; and ^P < 0.05 Interaction between treatment and sex.
