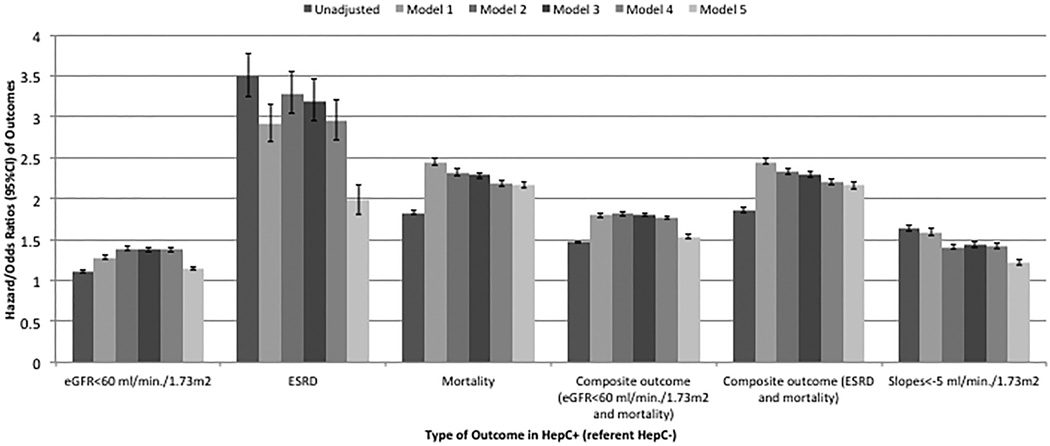
Figure 2.
Association of presence of HCV and outcomes using Cox-proportional models and logistic regression models in the cohort of 1,021,049 patients
Adjusted for:
Model 1: age, gender, race/ethnicity
Model 2: Model 1 and baseline GFR
Model 3: Model 2 and comorbidities (diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseae, congestive heart failure, cerebro-vascular disease, peripheral vascular disease, lung disease, dementia, rheumatic disease, malignancy, HIV/AIDS and depression)
Model 4: Model 3 and systolic BP, diastolic BP and BMI
Model 5: Model 4 and socio-demographic parameters (income, marital status, service connection, complience, drug complience, number of visit, number of medication and ACEI/ARB usage)
Abbreviations: ACEI: Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; AIDS: Acquired immundeficiency syndrome; ARB: Angiotensin receptor blocker; BMI: body mass index; BP: blood pressure; eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate; HIV: Human Immundeficiency Virus