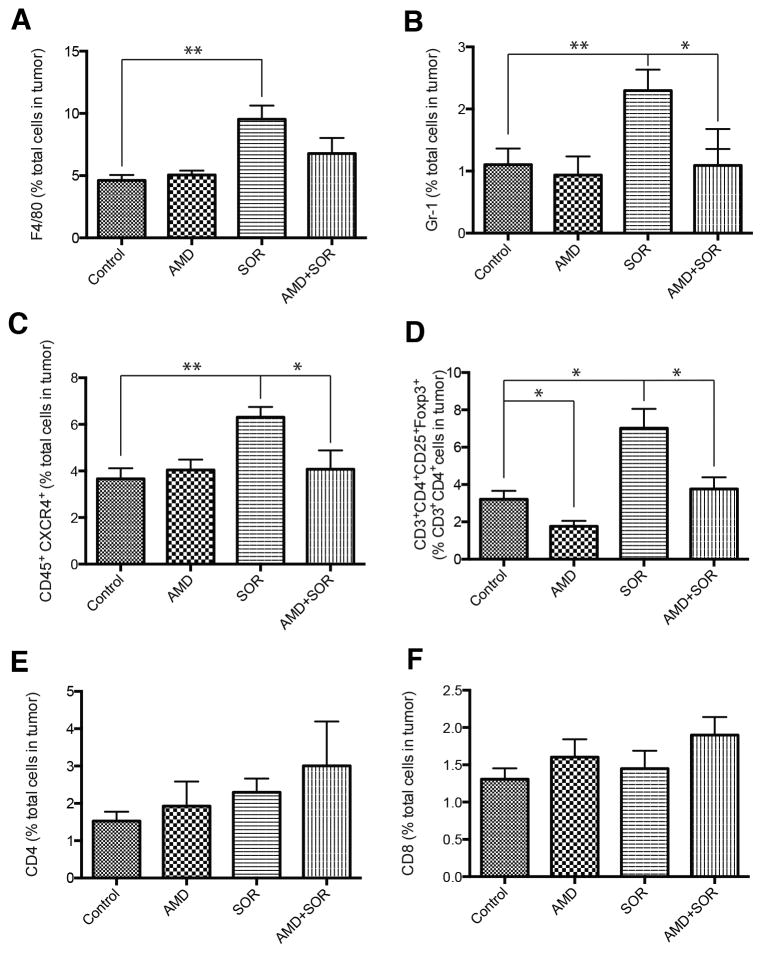
Figure 2. Sorafenib treatment induces a polarization towards a pro-immunosuppressive environment in orthotopic HCA-1 tumors, which is prevented by CXCR4 inhibition in the face of persistent hypoxia.
(A–D) Changes in viable tumor-infiltrating immune cells in HCA-1 tumors from mice treated with sorafenib with or without AMD3100 versus control analyzed by flow cytometry. The number of 7AAD–CD45+F4/80+ tumor-associated macrophages (A), 7AAD–CD11b+Gr1+ monocytes (B), 7AAD–CD45+CXCR4+ cells (C), and 7AAD–CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ T regulatory (Treg) cells (D) significantly increased in sorafenib treated HCCs. Combining AMD3100 treatment with sorafenib prevents these effects. (E–F) The number of 7AAD–CD4+CD3+ (E) and 7AAD–CD8+CD3+ (F) T lymphocytes was not significantly different between the four treatment groups in HCA-1 HCCs. *p<0.05; Data are shown as mean±SEM.